1. A War Problem

During World War II, the United States faced a serious challenge. Precision bombing was difficult before the rise of computers or smart weapons. Each missed target meant wasted effort and loss of life. Scientists were told to think creatively, to find something new that could change the course of battle. Among them stood psychologist B.F. Skinner, a man fascinated by how behavior could be shaped through reward and repetition. His idea seemed outrageous at first, but it held promise. What if animals could be trained to guide bombs to their targets? It sounded unbelievable, yet Skinner’s curiosity set the stage for one of the strangest and most fascinating experiments in wartime history.
2. Enter B.F. Skinner

B.F. Skinner was already known for his groundbreaking work in behavioral psychology. He believed that all actions, whether human or animal, could be influenced by reward. When the U.S. military sought innovative ways to improve bomb accuracy, Skinner proposed something no one expected. Instead of machines, he suggested using pigeons. He had trained them before to complete complex tasks by rewarding correct behavior. To him, there was nothing strange about extending this method to warfare. Skinner’s confidence wasn’t arrogance, but conviction born from science. He knew that patience, structure, and reinforcement could teach even simple creatures to do extraordinary things. The military hesitated, but curiosity eventually opened the door to his wild idea.
3. The Training Begins

In a quiet lab, Skinner started training pigeons using projected images of ships and targets. Every time a pigeon pecked at the correct spot on the image, it received a food reward. Over time, the birds learned to recognize and peck precisely at enemy targets. Their focus was remarkable. They ignored distractions and responded instantly to what they saw. Skinner’s approach proved that behavior could be controlled through reinforcement. Each peck became evidence that learning was not limited to humans. The pigeons’ accuracy improved rapidly, and soon, their performance caught the attention of officials. It was clear that Skinner’s idea, while strange, might actually change how technology and nature could work together.
4. Project Pigeon Takes Flight
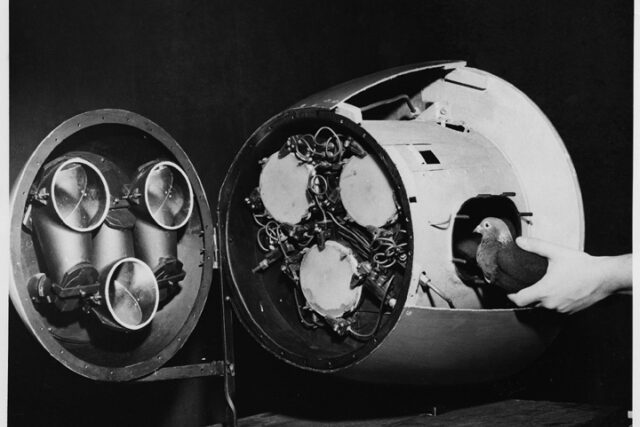
After seeing potential in Skinner’s work, the U.S. military approved his proposal under the code name Project Pigeon. The plan involved placing trained pigeons inside the nose of a bomb. They would watch a screen showing a moving image of the target and peck to correct its course. The pigeons’ pecks sent signals to adjust the bomb’s fins, keeping it on track. It was a clever mix of biology and mechanics. In trial runs, the pigeons performed impressively, tracking targets with steady focus. It seemed the project might actually succeed. Though unconventional, Skinner’s birds were proving to be reliable, disciplined, and surprisingly intelligent in their assigned roles.
5. Incredible Accuracy

The pigeons exceeded all expectations. During controlled tests, they followed targets with almost flawless precision. They didn’t lose focus, grow tired, or become distracted. While early mechanical systems often malfunctioned, the birds stayed consistent. For a simple food reward, they performed with a level of accuracy that amazed everyone watching. Skinner was thrilled, not only because his theory worked, but because the pigeons demonstrated learning and discipline beyond what anyone imagined possible. His findings suggested that nature’s creatures, when properly trained, could outperform early technology. The project was gaining credibility, even if its concept still made people laugh behind closed doors.
6. Too Strange to Fund

Despite their remarkable performance, the project’s future grew uncertain. Military officials were uneasy about the idea of birds controlling bombs. It seemed too absurd to take seriously. Leaders worried about public perception more than scientific merit. They chose to pursue more conventional technologies, even though they weren’t as reliable at the time. Skinner tried to defend his project, but he was ultimately ignored. Project Pigeon was shelved. Skinner later reflected that the world simply wasn’t ready for ideas that challenged its imagination. What could have been a revolutionary system became another forgotten story of innovation cut short by disbelief.
7. The Science of Conditioning

Even though Project Pigeon ended, its legacy reshaped science. Skinner’s experiment proved that behavior could be modified through structured reinforcement. Every peck, every reward, revealed how powerful conditioning truly was. His findings extended beyond warfare and became the foundation for modern behavioral psychology. Scientists and educators began applying his principles to understand motivation and learning. Skinner showed that consistent reinforcement could produce predictable, repeatable results. The pigeons may not have guided bombs, but they guided a new way of thinking about how all creatures, including humans, learn. Their contribution outlived the project itself, influencing fields far beyond the military.
8. From Bombs to Classrooms

After the project’s cancellation, Skinner turned his focus to education. He wondered if the same reinforcement principles could help students learn better. He created early “teaching machines” that rewarded correct answers with instant feedback. The concept was simple but transformative. Just like the pigeons learned through positive reinforcement, students could be motivated to keep learning through small rewards. His ideas became the foundation for personalized education and interactive learning systems. The pigeons’ training methods found new life in classrooms, showing how wartime innovation could unexpectedly improve peacetime knowledge.
9. The Rise of Gamification

Today, we see Skinner’s ideas everywhere. From fitness apps to social media, rewards keep users engaged. Points, likes, and badges mimic the same conditioning used in Project Pigeon. Each small success encourages us to keep going, just as the pigeons pecked for food. The system isn’t manipulation, it’s motivation. It reminds us that behavior thrives on feedback. Every ping or notification mirrors Skinner’s methods. His experiment, once dismissed as odd, laid the groundwork for how modern technology holds our attention. In a way, every tap, scroll, and click still echoes the lessons his pigeons taught decades ago.
10. The Pigeon Legacy in AI

Project Pigeon also laid an early foundation for artificial intelligence. The pigeons served as living processors, interpreting visual information and adjusting their actions based on feedback. Today’s AI systems function the same way, only with faster calculations and endless memory. Skinner’s pigeons represented the first biological model of adaptive learning. What once relied on feathers and food now depends on code and data. His vision of feedback-driven control lives on in drones, robotics, and autonomous systems. The world may have moved on from pigeons, but their role in inspiring machine intelligence remains quietly powerful.
11. Military Tech Parallels

Modern missile guidance systems owe something to Skinner’s original idea. The concept of tracking, adjusting, and correcting a target’s course through feedback still defines precision technology today. Cameras and sensors now replace pigeons, but the principle is identical. Skinner was decades ahead of his time. While the military dismissed his work, they eventually embraced its logic. The difference was that machines made the process cleaner and easier to explain. Yet, behind every smart system, the spirit of those pigeons remains, a reminder that even strange ideas can predict future breakthroughs.
12. A Lesson in Open-Mindedness

Project Pigeon’s rejection was not due to failure but fear of ridicule. Leaders couldn’t bring themselves to trust such an unconventional approach. It’s a familiar pattern in innovation: ideas that sound too strange often get ignored until someone else proves them right. The story became a timeless reminder to stay open-minded. Many breakthroughs begin as jokes or doubts. Skinner’s pigeons may not have changed warfare, but they changed how we think about creativity and possibility. The experiment taught that genius sometimes looks ridiculous until time catches up to it.
13. The Ethics of Animal Use
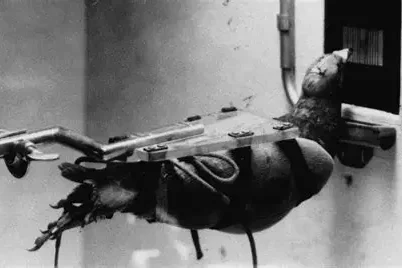
Looking back, Skinner’s work raises questions about how far humans should go when using animals in research. While his pigeons were treated humanely, the idea of involving them in war feels unsettling today. Modern science now follows stricter guidelines, ensuring animals aren’t exploited for experimentation. Yet, Skinner’s pigeons highlight an important balance between progress and ethics. Innovation must respect life while exploring new frontiers. Their story encourages reflection on how curiosity can sometimes overlook compassion, and how both must coexist in any responsible pursuit of discovery.
14. Conditioning in Everyday Life

The principles that shaped Skinner’s pigeons still shape us. Every time we check a phone, refresh a feed, or crave a like, we are responding to the same conditioning that trained those birds. Small rewards keep us engaged. The cycle of cue, response, and satisfaction is now digital. Skinner’s experiment predicted our relationship with technology, showing how reinforcement can control habits without us noticing. It’s humbling to realize that we are not so different from the pigeons that once pecked for food, we just do it through screens instead.
15. From Pigeons to Pilots

While Skinner’s pigeons never guided bombs, real pigeons played crucial roles in the war. They delivered messages across battlefields when radio communication failed. Their reliability saved countless lives. This legacy gave weight to Skinner’s belief that pigeons were intelligent, trainable, and trustworthy. His work simply took that truth in a new direction. Even though his version never made it into combat, it highlighted the quiet brilliance of a species often overlooked. Pigeons proved that loyalty and focus are not limited to humans.
16. What the Pigeons Proved

Project Pigeon proved that intelligence comes in many forms. The pigeons didn’t reason or plan, yet their actions showed precision through practice. Skinner demonstrated that focus, repetition, and reward could produce results as impressive as human skill. It was proof that learning doesn’t always require conscious thought. Sometimes, consistency is smarter than complexity. The project reminded the world that patience and discipline can achieve wonders when guided by clear feedback. The pigeons became small but powerful symbols of progress born from simplicity.
17. Echoes in Modern Science

Skinner’s influence continues across psychology, education, technology, and design. From animal trainers to app developers, his methods shape how we teach, motivate, and engage. The pigeons that once pecked at screens unknowingly sparked an understanding of behavior that touches nearly every modern system. Their lessons ripple through classrooms, therapy, and artificial intelligence. What began as a strange wartime experiment became one of the most significant breakthroughs in understanding human and animal behavior alike. The pigeons proved that science and curiosity can transform even the most unusual ideas into timeless wisdom.
18. The Final Lesson
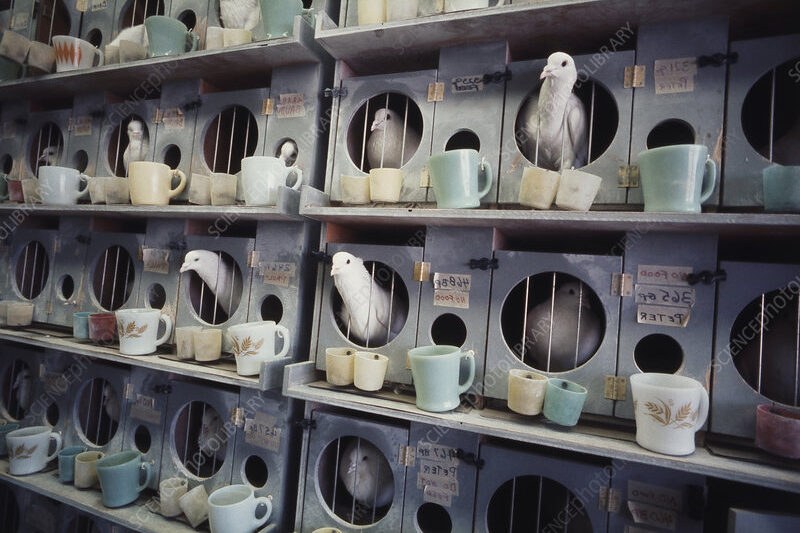

Skinner’s pigeons never saw battle, but their legacy soared far beyond war. They revealed how feedback, structure, and persistence could unlock potential in both animals and humans. Their experiment bridged psychology and technology, proving that progress often starts with unconventional thinking. The pigeons’ story is a reminder that every great discovery begins with a question no one dares to ask. Sometimes, the smallest creatures leave the largest lessons. Their journey from the lab to history books shows that brilliance can take flight from even the most unexpected places.
This story WWII’s Secret: Pigeons That Nearly Guided Bombs was first published on Daily FETCH


