1. We Are Already Becoming Part Human, Part Machine
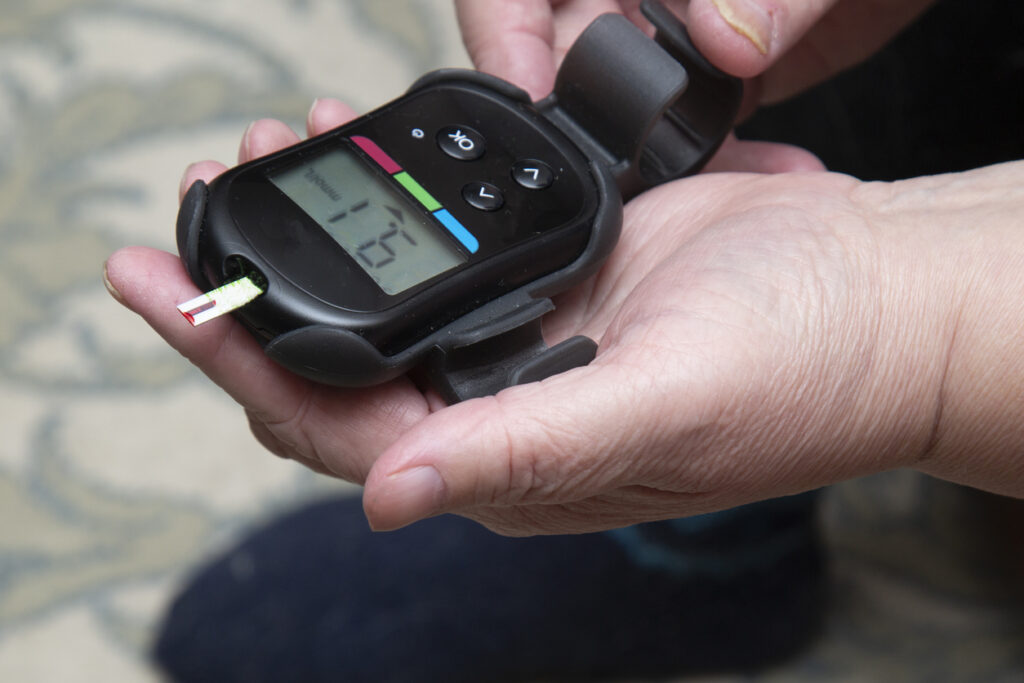

Wearable medical devices like continuous glucose monitors, self-adjusting hearing aids, and smart insulin pumps blur the line between human and machine. These devices use sensors and algorithms to monitor and respond to your body’s needs in real time, no user input required. They’re not sci-fi concepts anymore; they’re today’s quiet reality. These “cyborg” tools can significantly improve quality of life. For someone with diabetes, a glucose sensor relays data to a pump, which adjusts insulin without manual intervention. Similarly, hearing aids now automatically tune themselves in noisy environments. These advances demonstrate how intimate, machine-enhanced healthcare has quietly become part of our routines.
2. Smartwatch = Health Hub
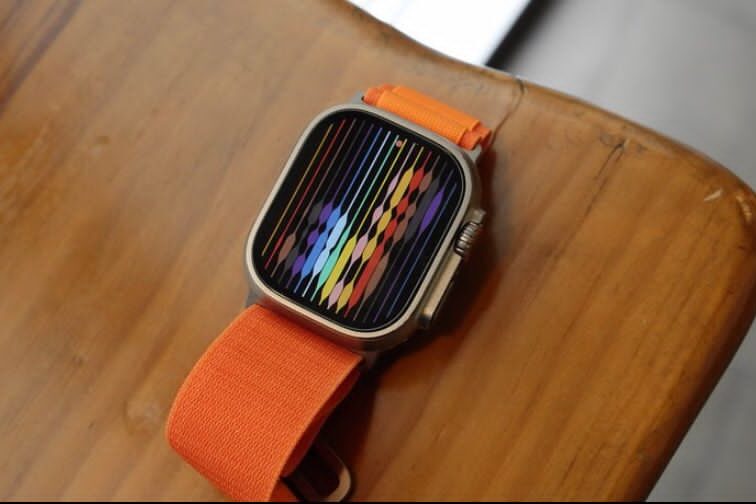

Your Apple Watch, Oura ring, or similar wearable does more than tell time, it tracks heart rate, sleep quality, blood oxygen levels, stress, and even indicators of illness before symptoms appear. It’s continuously collecting data, analyzing trends, and alerting you when something seems off. That early warning can be life-changing. For example, your watch might detect an elevated resting heart rate and prompt you to see a doctor before you even feel sick. Some apps even remind you to stand more, hydrate, or take deep breaths when they sense stress. These devices are becoming essential partners in your health journey.
3. Snack‑Delivering Robots
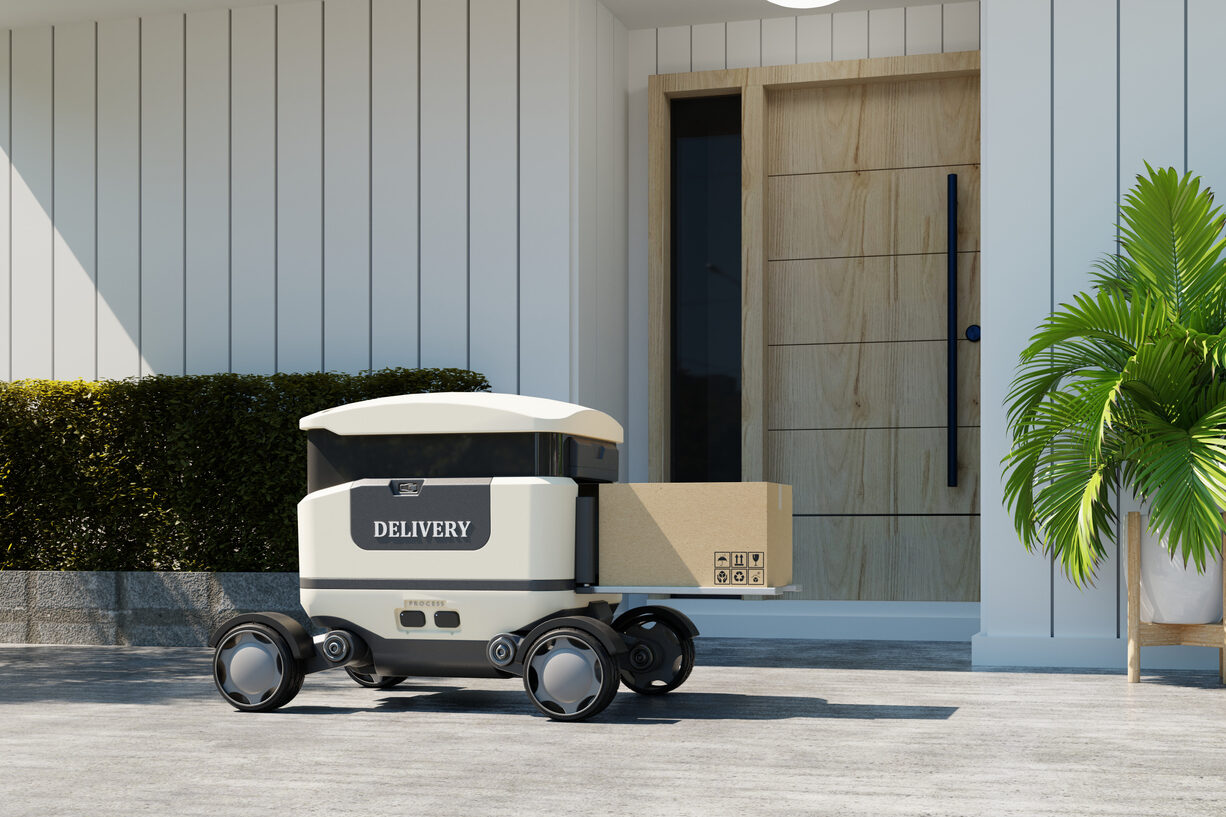

Those compact, boxy delivery bots zipping across sidewalks aren’t just tech demos, they’re operational drivers of convenience. Found on college campuses and in suburban neighborhoods, these autonomous carts navigate around pedestrians, traffic, and even weather. They’re changing how we think about delivery. Instead of waiting for a person, your coffee or snack arrives via a robot that follows sidewalks, senses obstacles, and operates independently. It’s not sci‑fi, it’s a practical, contactless way to get what you need.
4. Training Your AI Twin
Every message, voice memo, and email you send helps train AI to imitate you. Machine learning models analyze patterns in your tone, word choice, and writing style to build personalized replicas of your voice and communication habits. This tech can be helpful, automating responses or drafting messages for you, but it also raises privacy concerns. As these AI doubles begin replying to messages or generating texts in your voice, you might start questioning where the human ends and the machine begins.
5. Robot Taxis Are Here
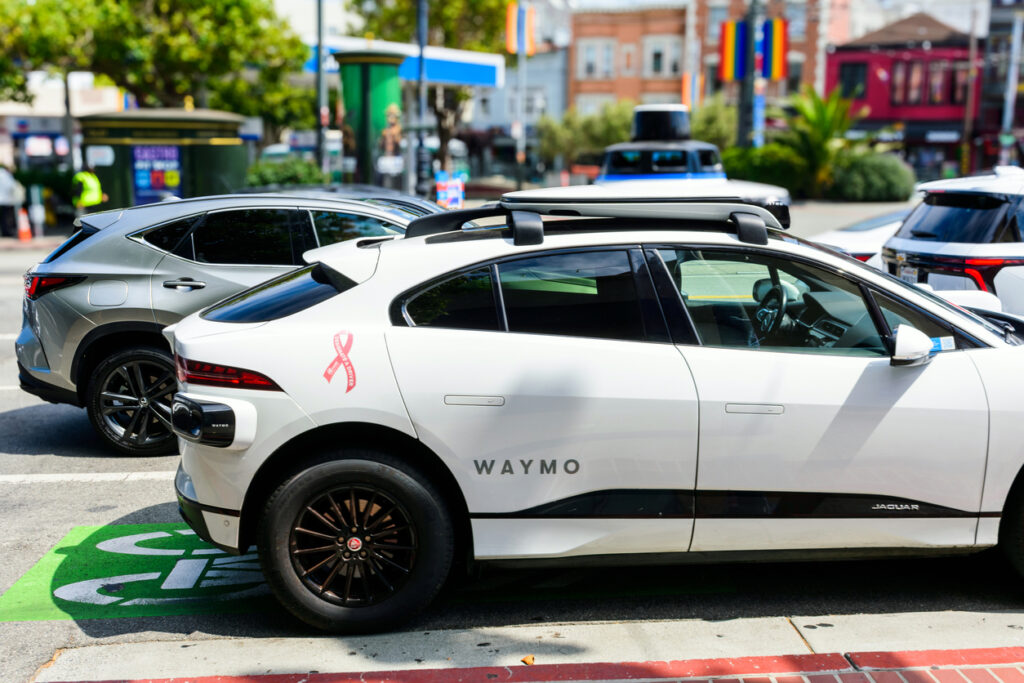

Driverless taxis from companies like Waymo and Cruise are operating in several cities, Phoenix, San Francisco, Los Angeles, and Austin, without anyone behind the wheel. These robotaxis are being hailed through apps, offering fully autonomous trips. Waymo alone operates over 1,500 vehicles, logging millions of miles and delivering hundreds of thousands of paid rides weekly. They’ve even driven more than 100 million miles without a human driver. While regulatory and technical hurdles remain, the vision of seamless, on-demand robotaxis is already unfolding around us.
6. AI Companions as Partners

AI chatbots like Replika, Character.AI, and Grok have become emotional substitutes for loneliness, romance, grief, or daily conversation. In Washington, D.C., for example, about 28% of singles report flirting or forming romantic connections with AI companions, showing how pervasive these relationships are becoming. These tools can offer comfort, consistency, and emotional support, some users even describe chatbot partners as more reliable than humans. Yet studies show risks too: heavy users, especially those with limited real-world social connections, may end up more isolated and emotionally dependent.
7. Smart Wearables Are Passive Doctors

Stress alerts, hydration reminders, breathing prompts, wearables like the Apple Watch and Oura ring monitor your health around the clock. They spot heart-rate irregularities, track sleep disturbances, and can predict illness before symptoms appear. These devices feel like wellness tools, but they’re also surveillance systems hiding in plain sight. They constantly collect biological data, analyze behavior, and can deliver alerts, or even advice, based on your physiology without you actively engaging.
8. Cultured Meat on the Menu
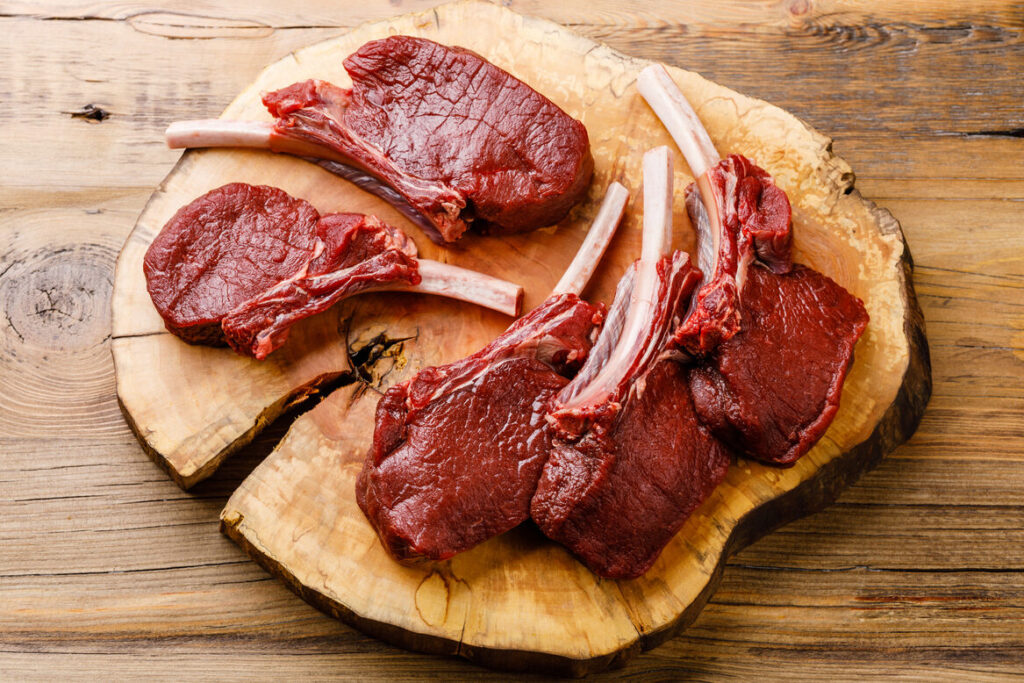

Lab-grown meat is no longer fantasy, it’s landing on real plates. In April 2025, Vow’s cultured quail received regulatory approval in Australia and New Zealand, with restaurant service in Sydney and Melbourne beginning by mid‑June. Meanwhile, Wildtype’s cultivated coho salmon gained FDA approval in the U.S. in late May, and soon appeared on menus at a Portland restaurant. These meats are grown from animal cells in clean bioreactors, no slaughter needed. Diners in select venues now enjoy the same textures and flavors as conventional meat. While production is still limited and costs are high, these launches mark the first steps toward mainstream availability and a more sustainable food system.
9. Popular Virtual Influencers
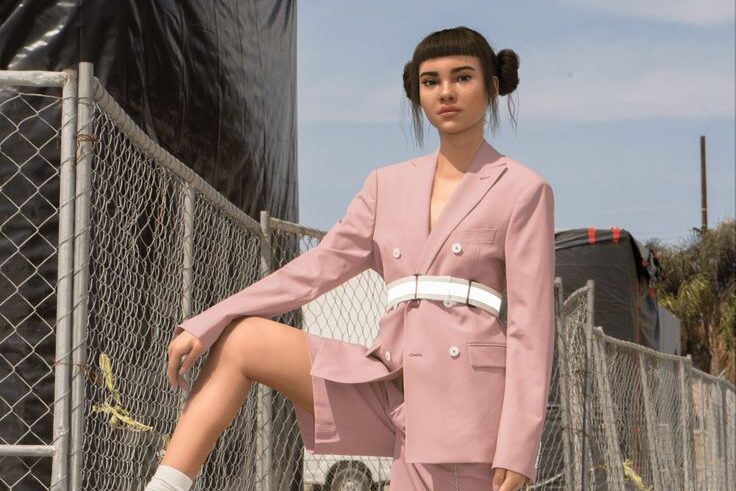

Virtual personalities like Lil Miquela are topping social feeds, even though they don’t exist in real life. Miquela has millions of followers, models for Prada and Diesel, releases music, and even takes part in brand‑level campaigns like BMW iX2, all while being entirely CGI. Brands love CGI influencers because they offer consistent control and avoid risks tied to human behavior. They can curate every image, post, and hashtag precisely. But critics worry about authenticity and transparency, as many followers may not realize these figures aren’t human.
10. Prosthetics That Respond to Thought
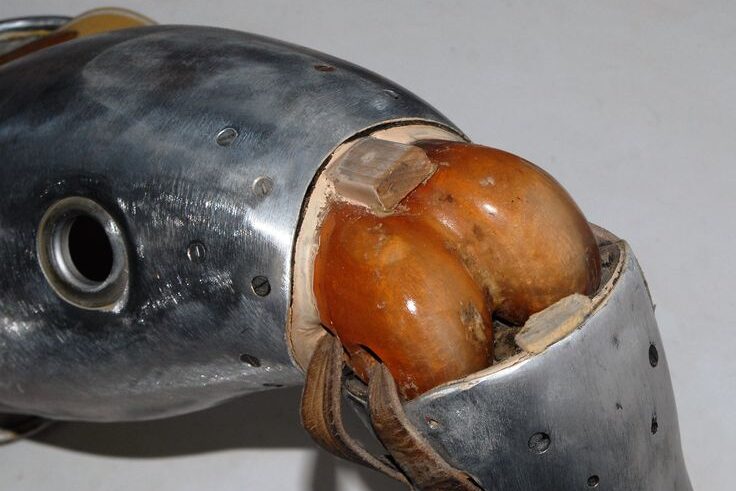
New prosthetic limbs are now controlled by nerve or muscle signals, enabling more natural, intuitive movement. The latest bionic knee, detailed in Science in July 2025, attaches directly to bone and nerves, allowing users to navigate stairs and obstacles more smoothly. Phantom Neuro is also developing muscle implants that let amputees control arm prosthetics with 93–98 % accuracy by decoding intent, without needing brain surgery. Clinical trials are expected in 2025. These advances move prosthetics from tools into seamless body extensions. Users report stronger ownership and a sense that the limb is part of themselves. Though widespread availability remains years off and costs are high, these technologies redefine the boundaries between people and machines.
11. Clone Your Voice with AI

AI voice tools like those from Respeecher or ElevenLabs let you replicate or borrow voices with uncanny realism. Widely used in film, gaming, and advertising, these tools are now powerful enough to reproduce someone’s tone, even deceased actors, with permission. Adoption by voice‑over artists is growing, though concerns around ethical use and consent are rising rapidly. Actors are negotiating usage terms carefully, fearing imitation could replace live performance. Some studios already include voice‑clone rights in contracts to guarantee fair compensation. Debates continue about ownership, licensing, and the blurred line between voice as labor and voice as likeness.
12. Earning Real Money in Virtual Worlds
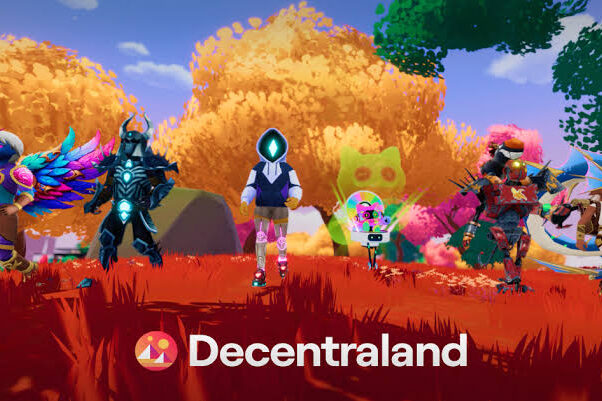

The metaverse and NFT-based games now power real-world economies. People buy, sell, and develop virtual land, art, and services, then convert those earnings back into physical-currency gains. Examples include virtual real estate trading in platforms like Decentraland and Sandbox, and NFT art selling for thousands, even six-figure sums. Some creators and players make livelihoods this way. In the Philippines, Axie Infinity players earned income by working as “scholars” in guilds, though financial instability and exploitative practices remain risks. As blockchain‑enabled virtual economies grow, the lines between digital worlds and real-life livelihoods keep fading.
13. Insects as Cyborg Scouts
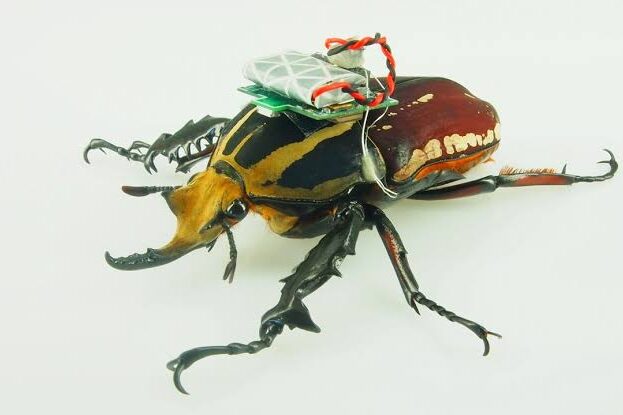

Scientists are now turning beetles into controllable micro-robots for possible use in search-and-rescue missions. Teams at the University of Queensland have developed “cyborg” beetles equipped with tiny electronic backpacks that steer them via electrodes in their antennae and wings. These beetles navigate rubble or tight crevices, spaces that are difficult for traditional robots, potentially accelerating rescue operations after building collapses or disasters. Real-world trials are expected within five years.
Researchers are also exploring more sophisticated navigation systems, using sensor-based gait analysis to guide cyborg insects autonomously in complex environments. With further development, these tiny rescuers could carry micro-cameras or sensors and act as first responders, combining insect agility with programmable control for tasks regular robots can’t manage.
14. Memory: Inserted or Recovered
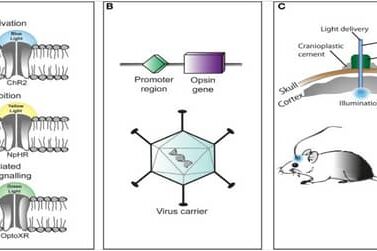
Recent studies using optogenetics have enabled scientists to implant false memories or recover “lost” early memories in mice. In one experiment, researchers activated specific hippocampal neurons linked to a prior neutral environment while delivering a mild shock in a different setting, causing the mouse to associate fear with the neutral context. In another study, memories from infancy that had faded over time were reactivated in adult mice using targeted light stimulation, showing memories may not be erased, only inaccessible.
While human applications are still speculative, these breakthroughs hint at future possibilities: restoring lost memories (such as in amnesia) or altering harmful memories (such as PTSD). But they also raise major ethical questions about identity, consent, and the potential psychological risks of manipulating neural data without clear boundaries.
15. AI as Muse: Creative Tools Empowering You

AI tools like ChatGPT, Midjourney, and Suno let anyone become a creator, from prose writers to visual artists to music composers. You can draft a story, design an image, or produce a song in seconds using simple prompts. These systems often collaborate with users, turning vague ideas into tangible works through generative algorithms. Artists from mainstream musicians to independent creators now use AI for inspiration, production, and editing. Some generate full songs or soundscapes with Suno or Udio; others blend visual styles through Midjourney. While not replacing human creativity, these tools enhance it, but they also spark debates about copyright, originality, and fair attribution.
This story The Future Is Now: 15 Sci-Fi Ideas That Quietly Became Real Life was first published on Daily FETCH


