
Concept Michael Gitter.
There are some species on this planet who do not use Oxygen to sustain life. Here are 15 of them.
1. Flatworms

Wikimedia Commons
Flatworms are versatile creatures that can survive in low-oxygen environments. They rely on anaerobic respiration, using alternative methods to generate energy when oxygen is scarce. Some species, such as freshwater planarians, can even regenerate parts of their body without needing oxygen. These worms are often found in stagnant or polluted waters, where oxygen levels are low. Their ability to adapt to hypoxic conditions makes flatworms an important part of aquatic ecosystems, where they play roles in decomposition and nutrient cycling, thriving in environments where many other organisms might not survive.
2. Brine Shrimp
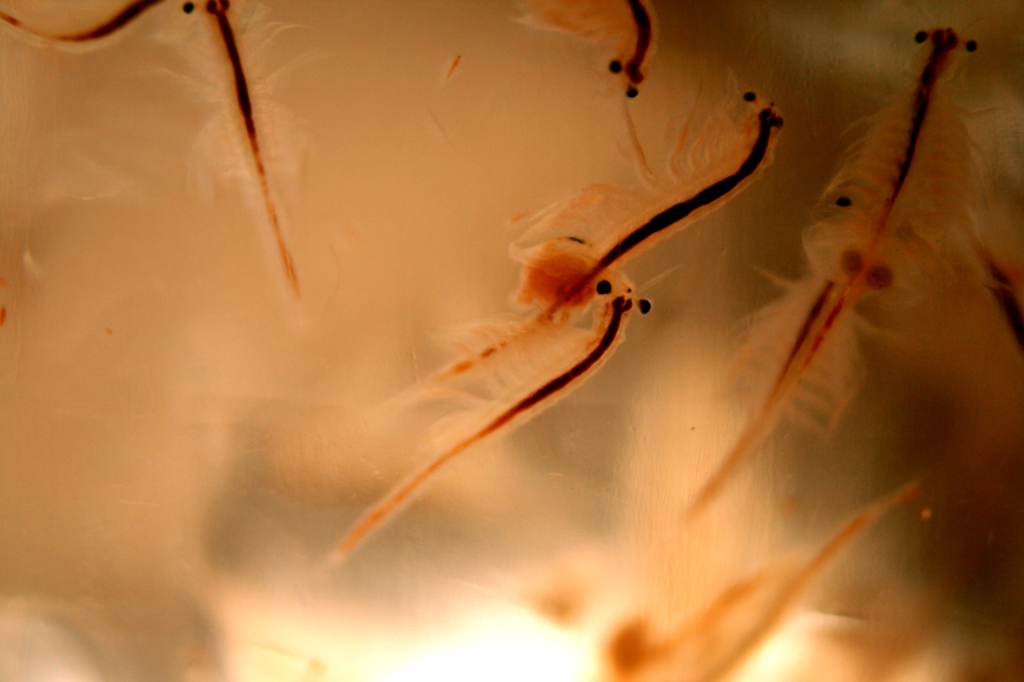
Wikimedia Commons
Brine shrimp, tiny crustaceans found in saltwater lakes, can survive in environments with very low oxygen. They have the ability to slow down their metabolism, allowing them to survive in oxygen-deprived waters. In extreme conditions, brine shrimp can even go into a dormant state, known as encystment, where they lose all metabolic activity until the environment becomes more hospitable. This ability to survive without oxygen makes brine shrimp highly resilient in their often harsh, saline habitats. Their adaptability is an impressive example of nature’s ingenuity in overcoming oxygen scarcity.
3. C. elegans (Nematodes)
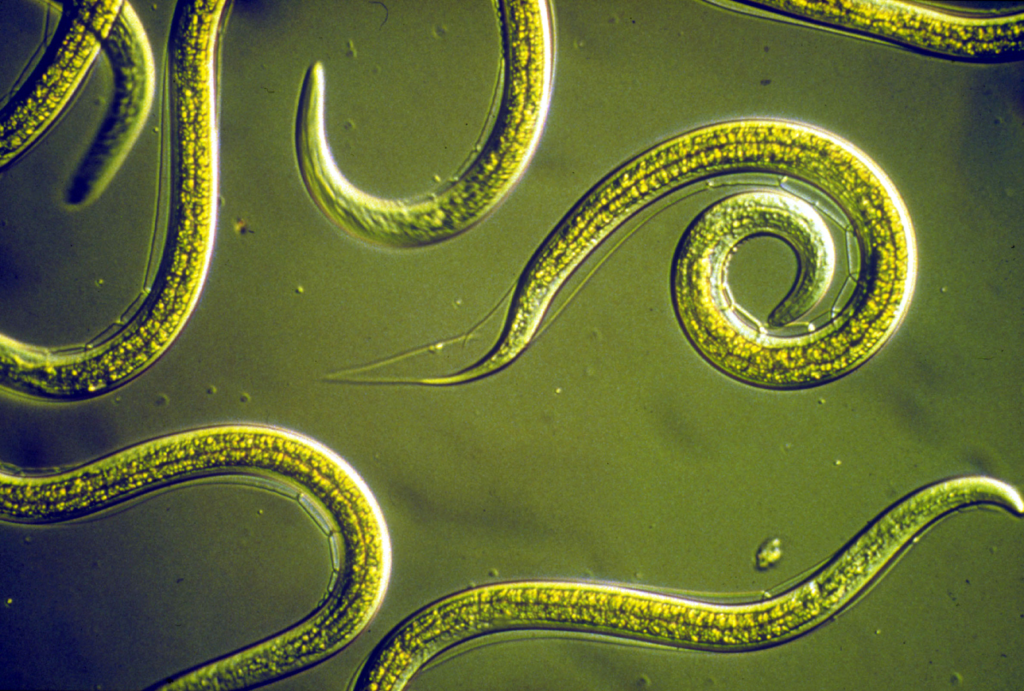
Wikimedia Commons
C. elegans, a type of roundworm, is a microscopic organism that can survive without oxygen for extended periods. In low-oxygen environments, these worms switch from aerobic to anaerobic respiration, allowing them to generate energy without the need for oxygen. This unique ability to use other chemical processes for energy is a key survival tactic. C. elegans also have the remarkable ability to repair damaged cells, making them resilient even in extreme conditions. Their adaptation to oxygen-poor environments has made them a popular subject of study in scientific research on stress and aging.
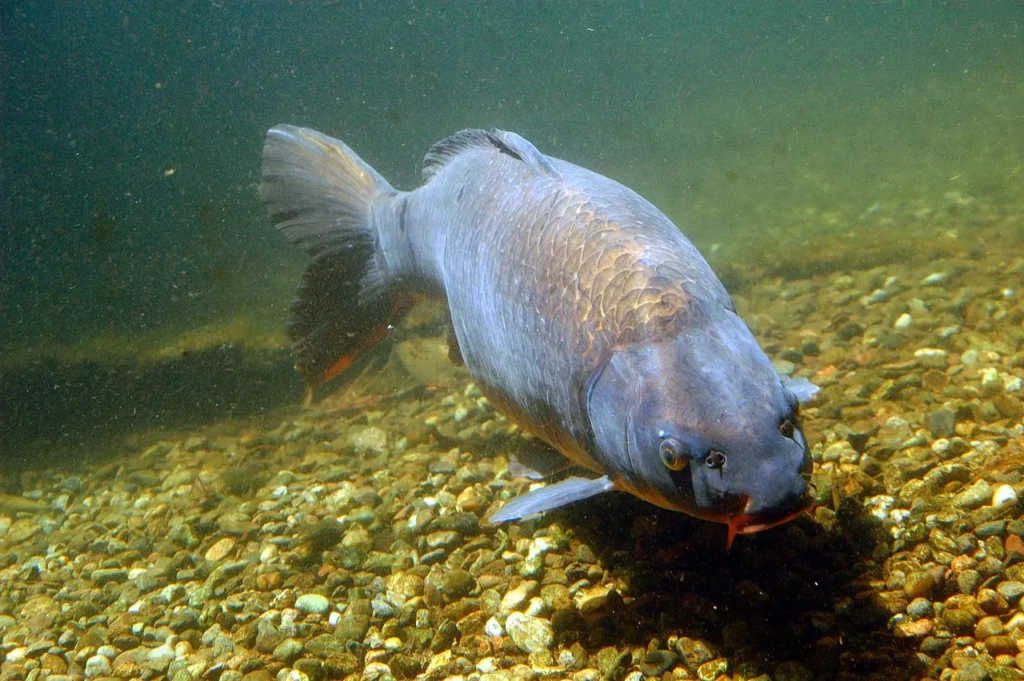
4. Certain Fish (Like the Carp)

Animalia
Carp and some other fish species are known for their ability to tolerate low-oxygen environments. In hypoxic conditions, these fish switch to anaerobic respiration, a process where they generate energy without relying on oxygen. While they still need oxygen to survive in the long term, carp can survive for extended periods in oxygen-deprived waters by using fermentation to process food. This allows them to thrive in stagnant ponds and polluted rivers where oxygen levels are low. Their ability to adapt to changing oxygen levels makes them highly resilient in challenging aquatic environments.
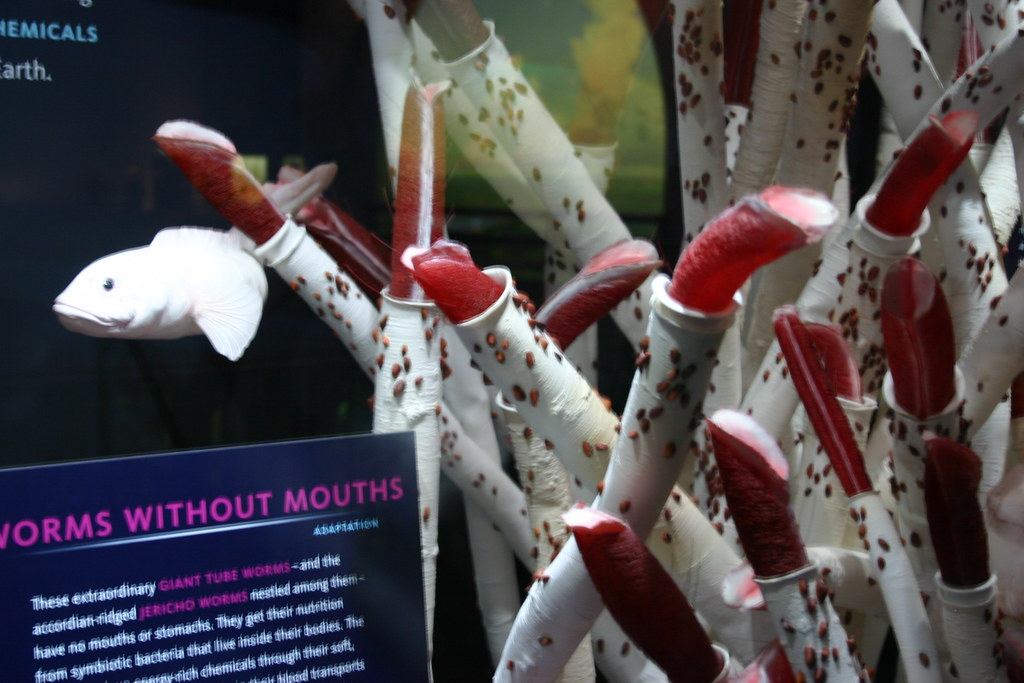
5. Giant Tube Worms

Flickr
Giant tube worms, found around hydrothermal vents deep in the ocean, thrive in environments with no oxygen. These worms don’t need oxygen to survive because they rely on symbiotic bacteria living inside their bodies. These bacteria convert hydrogen sulfide, found in the vent waters, into energy through a process called chemosynthesis. The tube worms absorb the nutrients from the bacteria, bypassing the need for oxygen entirely. Their ability to live in these extreme conditions, where no sunlight or oxygen is available, showcases the incredible adaptability of life in deep-sea ecosystems.
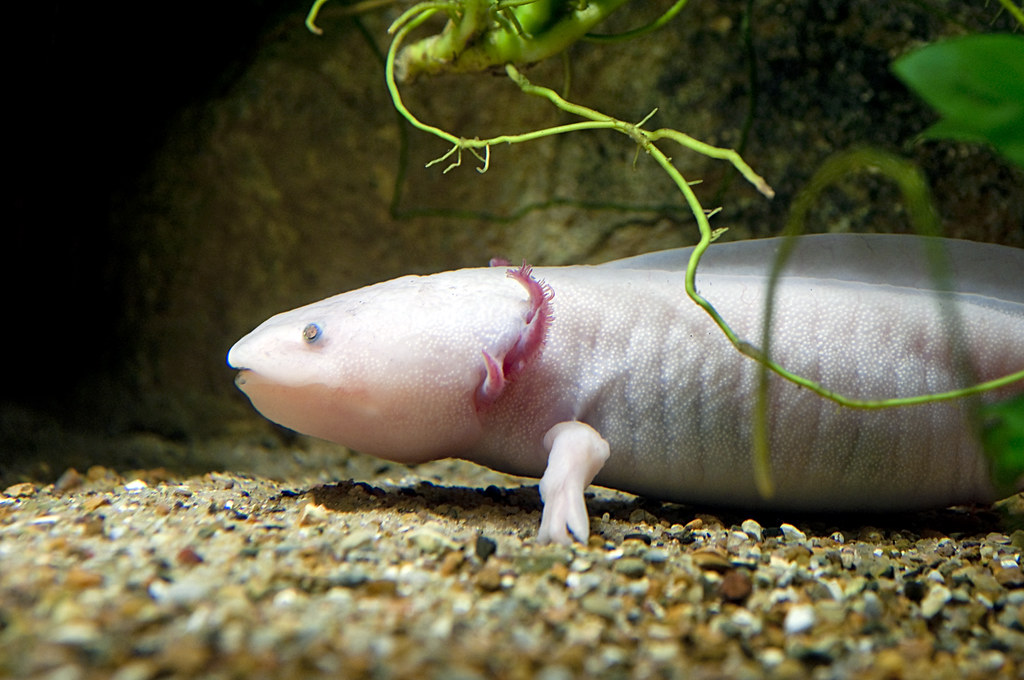
6. Axolotls

Flickr
Axolotls, aquatic salamanders native to lakes in Mexico, are known for their ability to survive in low-oxygen water. While they have gills for breathing, they can also absorb oxygen through their skin, allowing them to thrive in oxygen-deprived environments. They are also capable of regenerating lost limbs, spinal cords, and other organs, a fascinating trait that makes them a subject of scientific study. While axolotls can live without constant access to oxygen, they still require clean, cool water to maintain their health, showcasing their unique adaptation to low-oxygen conditions.
7. Lake Vostok’s Microorganisms

YouTube
Lake Vostok, located beneath Antarctica’s thick ice sheet, is a body of water that has been isolated from the outside world for millions of years. The extreme cold and lack of oxygen make it an inhospitable environment for most life forms. However, scientists have discovered microorganisms living in these frigid waters, surviving without oxygen. These microbes rely on chemical energy, such as hydrogen gas or methane, to fuel their metabolism. Their survival in such extreme conditions offers insight into the possibilities of life in other oxygen-deprived environments, such as on other planets.
8. Hydra
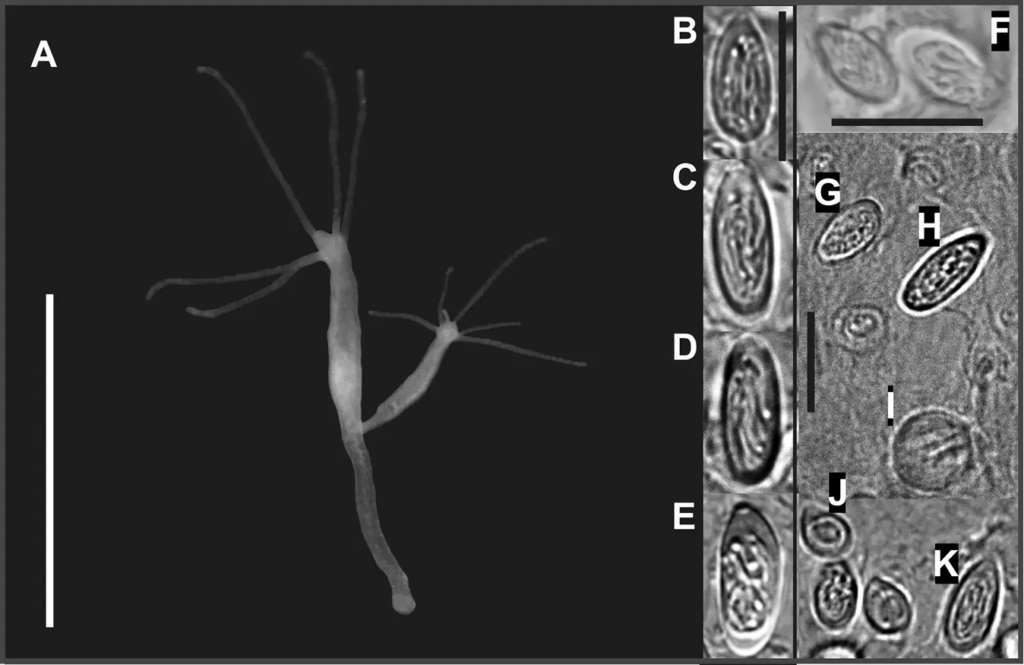
Animalia
Hydra, a simple freshwater organism, has remarkable survival abilities in low-oxygen environments. These tiny, multicellular animals are capable of anaerobic respiration, allowing them to thrive in water with minimal oxygen. Hydra can also regenerate their bodies, a process that occurs even in oxygen-deprived conditions. They rely on specialized cells for energy production and can survive in stagnant ponds or polluted waters where oxygen is scarce. Hydra’s ability to adapt to harsh environments, along with their regenerative capabilities, makes them an intriguing example of biological resilience in low-oxygen settings.
9. Clams (Like the Deep-Sea Mussels)

Flickr
Deep-sea clams and mussels that live around hydrothermal vents have adapted to survive in oxygen-poor environments. These animals rely on symbiotic bacteria within their bodies to produce energy through chemosynthesis, a process that doesn’t require oxygen. The bacteria convert hydrogen sulfide from the vent water into usable nutrients, providing the clams and mussels with food. In return, the clams provide the bacteria with shelter and other necessary conditions for survival. This mutualistic relationship allows these creatures to thrive in some of the most extreme, oxygen-deprived environments on Earth.
10. Lungfish
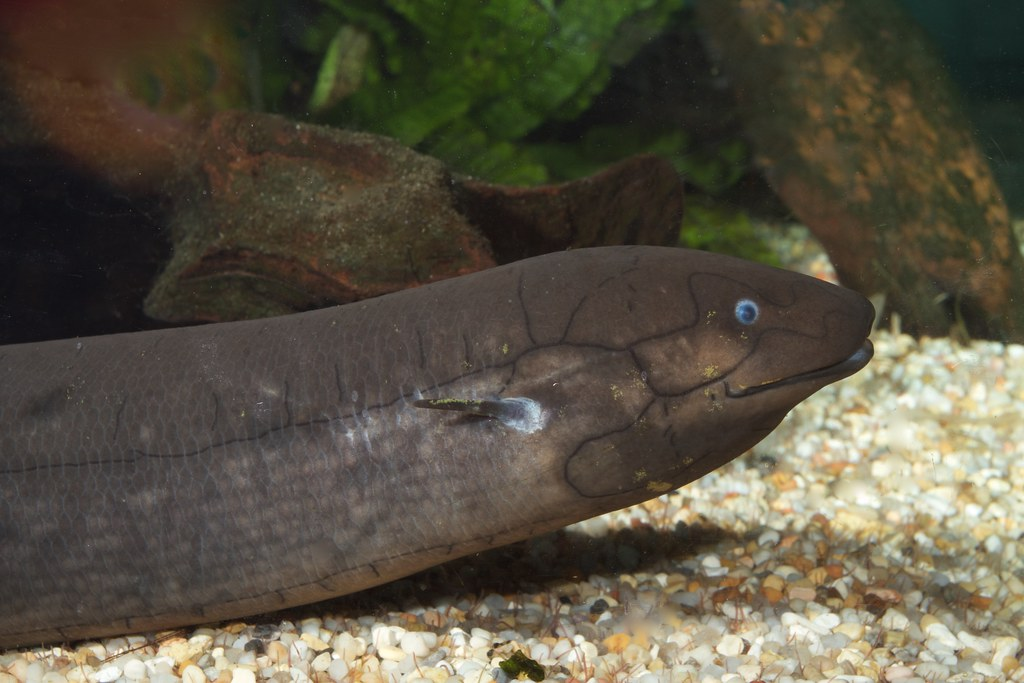

Flickr
Lungfish, found in parts of Africa and Australia, have an extraordinary ability to survive without oxygen for extended periods. These fish can live in dry, stagnant pools during droughts by burrowing into the mud and entering a state of dormancy. During this time, their metabolism slows significantly, and they rely on stored energy rather than oxygen. Some species of lungfish can even breathe air, using a primitive lung to extract oxygen when it becomes available. This remarkable ability to endure dry, oxygen-starved conditions helps lungfish survive harsh environments where other aquatic life cannot.
11. Spiny Anteater (Echidna)
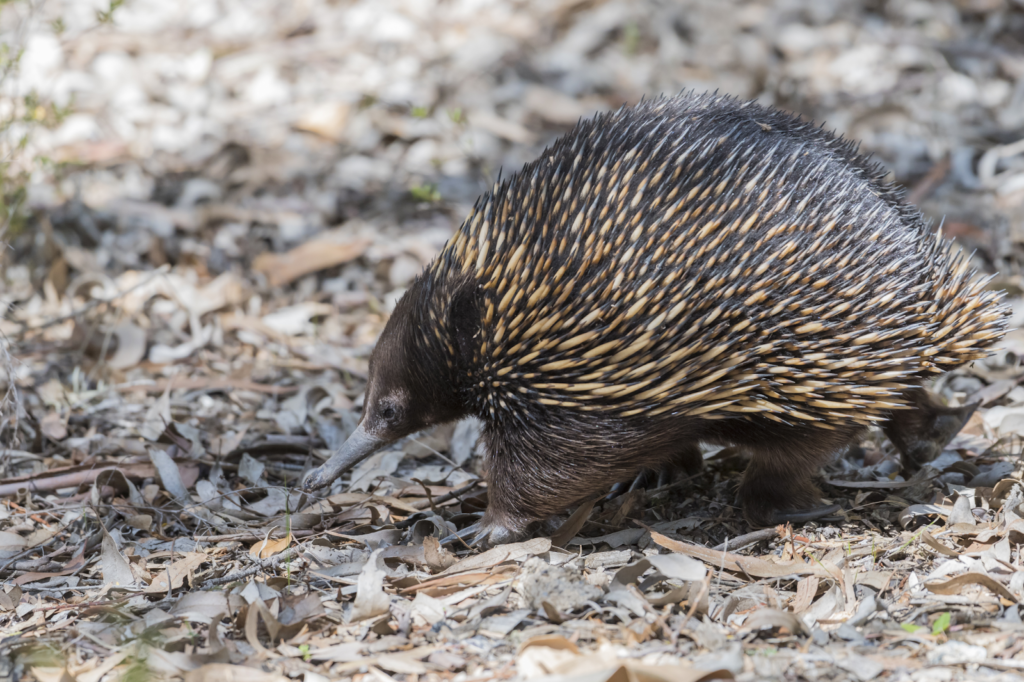

Wikimedia Commons
The spiny anteater, or echidna, can survive in environments with low oxygen, particularly during the colder months when food is scarce. To conserve energy, echidnas hibernate, slowing their metabolism and reducing their need for oxygen. This hibernation period allows them to survive in harsh conditions without actively searching for food. Although they still need oxygen to breathe, their ability to lower their metabolic rate during hibernation makes them adaptable to oxygen-poor environments. The echidna’s resilience showcases how animals can survive in challenging, low-oxygen environments by adjusting their bodily processes.
12. The Naked Mole Rat
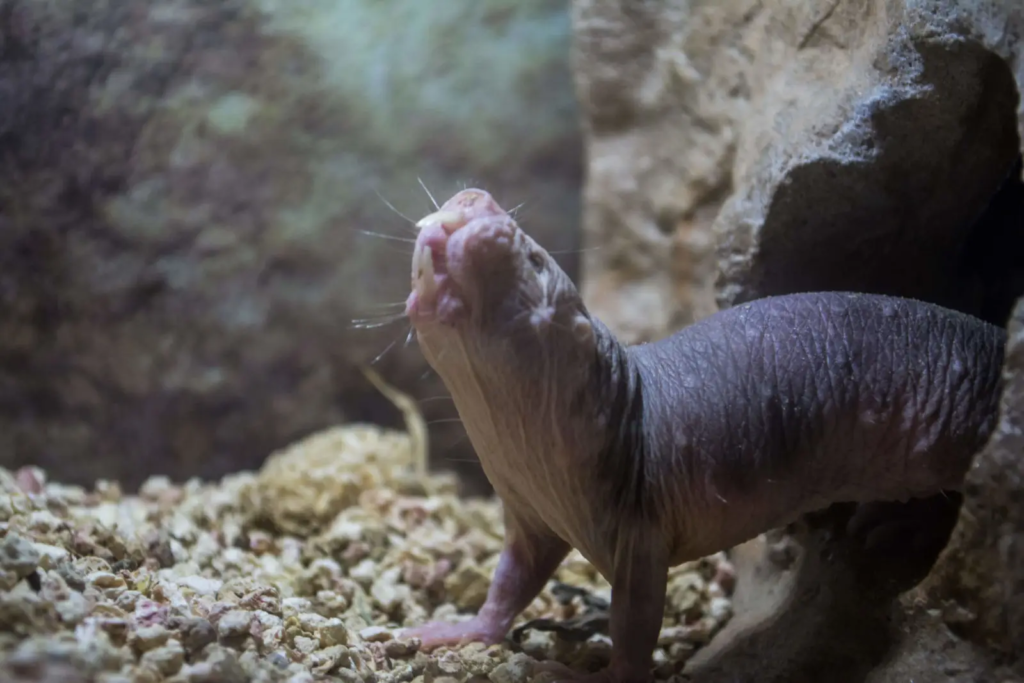

Animalia
Naked mole rats are fascinating creatures that can thrive in underground burrows where oxygen levels are extremely low. These highly social rodents have adapted to life without oxygen by using an efficient metabolic system that allows them to survive in hypoxic conditions. They are also unique in that they can function with lower levels of oxygen than most mammals. Their bodies have evolved to make the most out of available resources, and they are able to tolerate high carbon dioxide concentrations, making them one of the few mammals capable of living in such oxygen-deprived environments.
13. Tardigrades (Water Bears)

Flickr
Tardigrades, or water bears, are microscopic creatures that can survive in some of the most extreme conditions on Earth, including total absence of oxygen. When faced with harsh environments, they enter cryptobiosis, a state where they effectively shut down, halting all metabolic activity. In this state, they can survive in the vacuum of space, extreme radiation, and freezing or boiling temperatures. Once conditions improve, they “wake up” and resume normal function. Their ability to endure without oxygen makes them one of the most resilient organisms known to science.
14. Sea Cucumbers
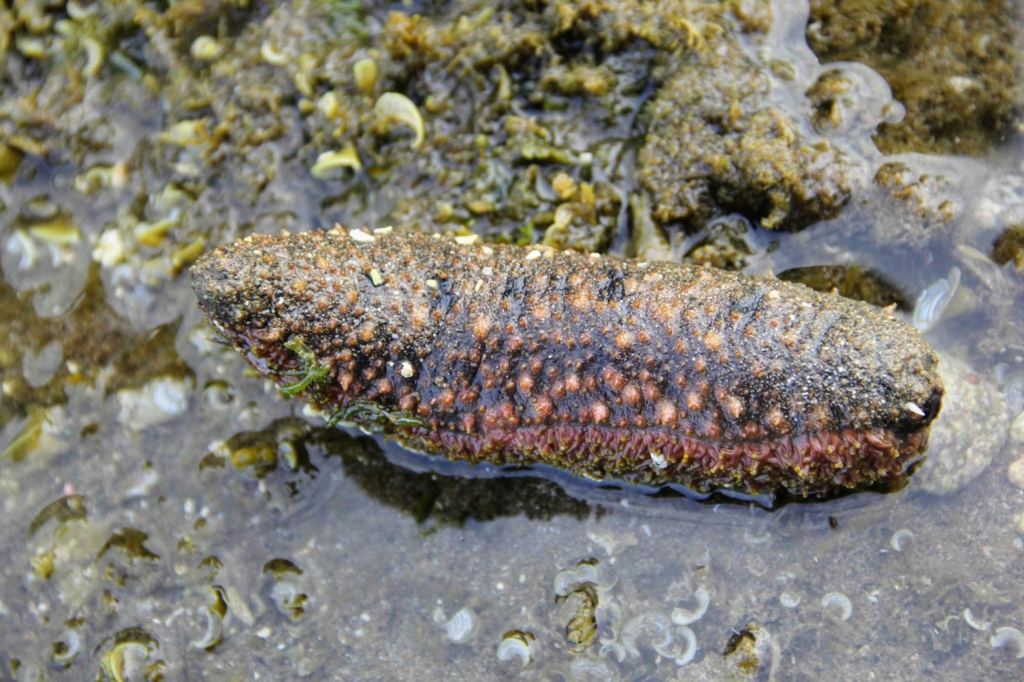

Wikimedia Commons
Sea cucumbers, marine creatures found on the ocean floor, can survive in low-oxygen environments, such as deep-sea habitats. They rely on anaerobic digestion to break down food in their intestines, allowing them to thrive where oxygen is scarce. These sea creatures are efficient scavengers, feeding on detritus and organic matter that settle on the ocean floor. Their ability to survive in oxygen-deprived waters allows them to play a vital role in deep-sea ecosystems, contributing to the breakdown of organic material and nutrient cycling in some of the world’s most remote environments.
15. Pfeiffer’s Smooth Earth Snake

YouTube
Pfeiffer’s smooth earth snake is a rare species that has adapted to survive in oxygen-poor soils. This non-venomous snake can live for long periods without oxygen by slowing its metabolism. It inhabits dense, low-oxygen soils, often burrowing into the ground where oxygen levels are minimal. By reducing its activity and metabolic rate, the snake can survive in conditions that would be inhospitable to most other animals. Its ability to function in hypoxic environments makes it a unique example of how certain species can adapt to life underground, where oxygen is limited.


