1. Wood Frogs – Masters of Winter Sleep
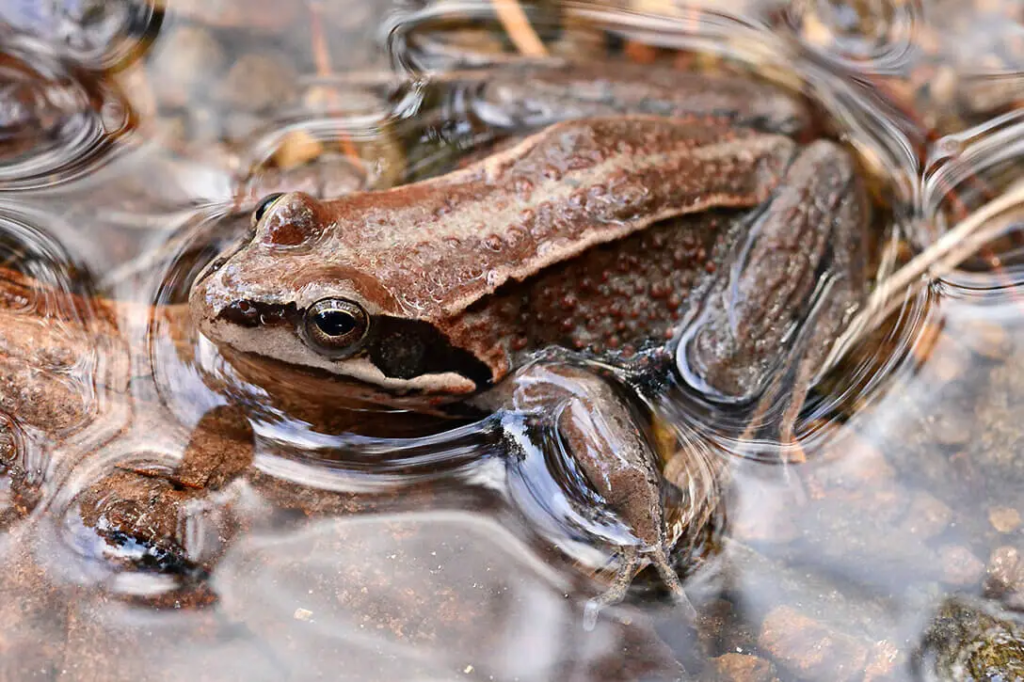

Wood frogs are some of the hardiest creatures on the planet, capable of surviving temperatures that dip below freezing. Native to North America, these little amphibians undergo a remarkable transformation when winter arrives. When temperatures drop, their bodies begin to freeze, starting with their extremities, and their hearts actually stop beating. But they’re not dead—they’re in a state of suspended animation. The wood frog’s body produces glucose, which acts like antifreeze, keeping its organs safe from damage as ice forms inside its cells. It may seem like the frog is lifeless, but it’s actually just waiting for warmer weather to thaw out. When the temperatures rise in spring, the frog “comes back to life,” its heart resumes beating, and it goes on as if nothing happened. This incredible adaptation allows wood frogs to endure some of the coldest winters in North America. They’re living proof that even in the harshest conditions, life can endure. The way they freeze and thaw is one of the most fascinating survival tactics found in the animal kingdom. These frogs are truly the definition of resilience, showing that even when frozen solid, life can still go on.
2. Tardigrades – Tiny Survivors of the Cold
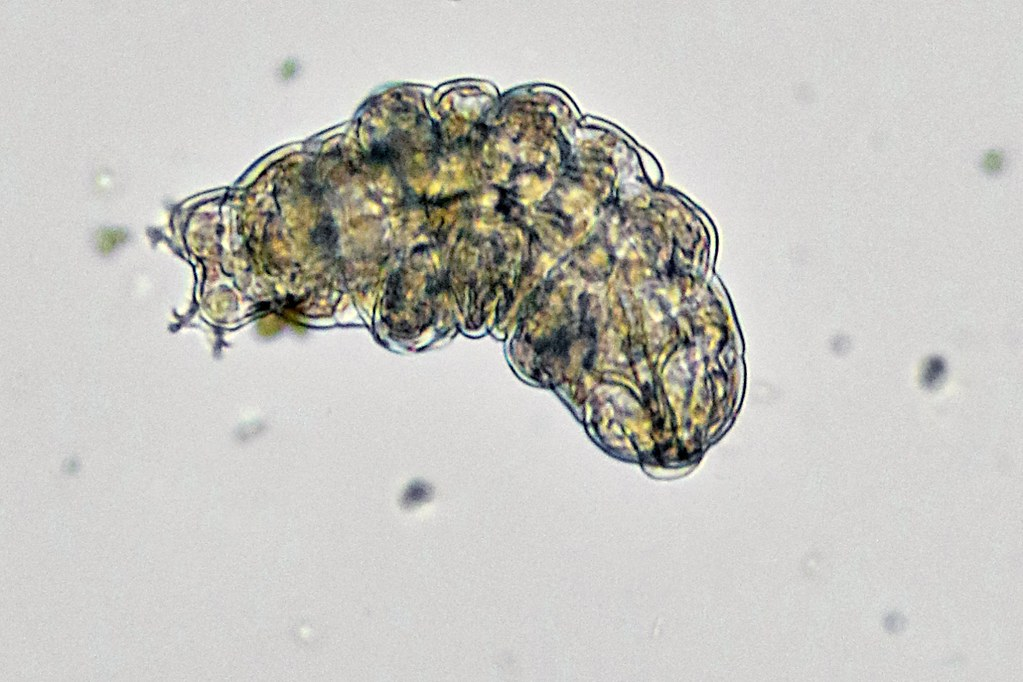
Tardigrades, or “water bears,” are microscopic creatures that can survive in some of the most extreme conditions on Earth, including freezing temperatures. These tiny, eight-legged animals are found in the coldest regions of our planet, but they’re also capable of surviving the vacuum of space and intense radiation. When faced with extreme conditions, tardigrades enter a state called cryptobiosis, where they essentially dry out and curl up into a ball. In this form, they can endure freezing temperatures, as well as dehydration and lack of oxygen. Their bodies become nearly indestructible, able to withstand being frozen solid for long periods. Even though they look like tiny little blobs, tardigrades are capable of surviving the harshest environments, thawing out when the temperature warms up and continuing their lives as if nothing ever happened. Scientists are studying their unique survival abilities in hopes of understanding how they might survive in extreme environments like those on other planets. Tardigrades are proof that life doesn’t always need warmth to survive—it can thrive in places most other creatures couldn’t even imagine. These resilient little beings show that even in the most inhospitable conditions, nature finds a way. From space to frozen landscapes, tardigrades are truly one of the universe’s greatest survivors.
3. Craneflies – Frozen for the Long Haul
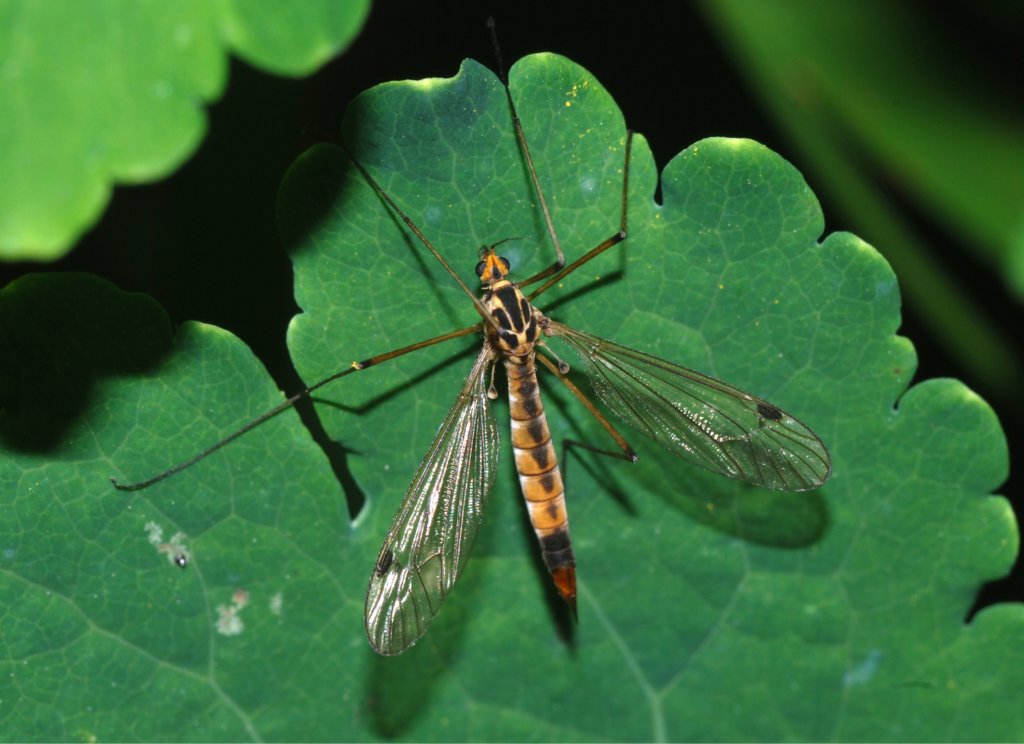

Craneflies may look like giant mosquitoes, but these insects have an extraordinary talent for surviving the cold, even freezing temperatures. Their larvae, which live in wet soils, can endure being frozen for months. This remarkable ability to survive subzero temperatures is due to special antifreeze proteins found in their bodies that prevent ice crystals from forming inside their cells. When the temperatures drop, the larvae go into a state of dormancy, effectively freezing themselves in place until warmer conditions return. Once thawed, the cranefly larvae continue their development as if nothing ever happened. This incredible adaptation allows them to survive the freezing temperatures of winter and continue their life cycle when the conditions improve. While they’re not the most famous survivors of the frost, craneflies are a testament to how even the most delicate creatures can adapt to extreme conditions. By “freezing” their bodies, they’ve found a way to outlast the cold and resume life in spring. Their ability to endure the harshest winters without suffering permanent damage is a true survival marvel.
4. Frostfish – Swimming in Freezing Waters
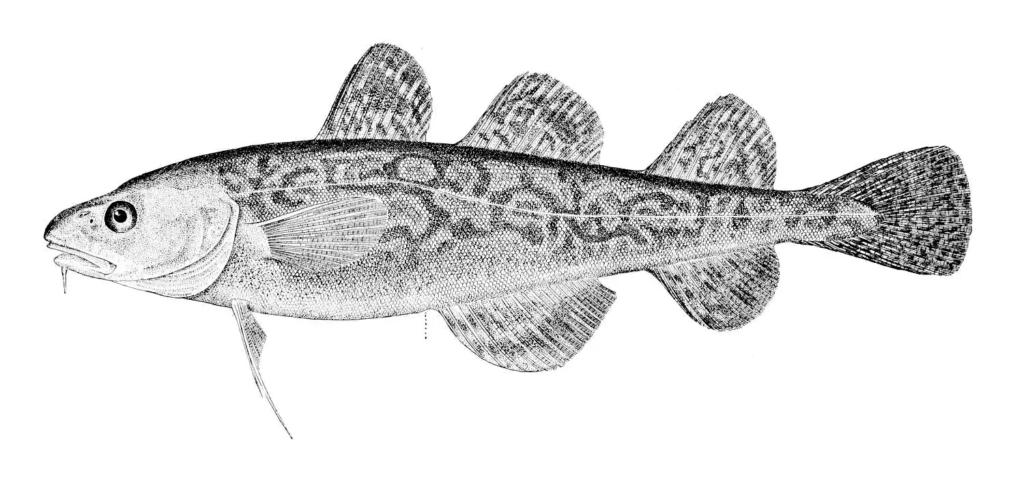
Frostfish, or icefish, are a unique group of fish native to the Southern Ocean around Antarctica, where the waters hover just above freezing. Unlike most fish, frostfish have evolved a special protein in their blood that prevents it from freezing, even in subzero temperatures. This antifreeze protein keeps their blood from turning into ice and helps them thrive in frigid waters that would freeze most fish solid. These fish don’t have red blood cells, giving their blood a clear, almost gelatinous appearance, which is part of their adaptation to survive in the cold. The frosty waters of the Antarctic would be uninhabitable for most marine life, but frostfish have adapted to these extreme conditions with ease. In fact, they are one of the few species that can live and reproduce in these icy depths. They are a vital part of the Antarctic ecosystem, providing food for larger predators like penguins and seals. As cold-blooded creatures, they depend on the environment to regulate their body temperature, and the frigid waters of the Southern Ocean are ideal for them. Their ability to survive in these icy conditions is a remarkable feat of evolution. It’s truly incredible how nature has created life that thrives in conditions where most other creatures would perish. The frostfish is a testament to the adaptability of life, even in the freezing waters of the Antarctic.
5. Snow Fleas – Tiny Survivors of the Frost

Snow fleas are small, often overlooked creatures that live in snowy environments, yet they’ve adapted to survive freezing temperatures like little winter warriors. Despite their name, snow fleas aren’t actually fleas—they’re a type of springtail, a tiny insect that can jump long distances. These creatures thrive in snowy, icy conditions where most other insects wouldn’t stand a chance. During the winter months, snow fleas become part of the snowpack, where they can survive freezing temperatures that would kill most other insects. They do this by producing a special protein that prevents their bodies from freezing. This ability to “supercool” their bodies means they can withstand extreme cold without being damaged. Snow fleas are also able to move around in the snow, hopping from one patch to another, seemingly oblivious to the frigid temperatures. Their small size and ability to endure freezing temperatures make them an important part of the winter ecosystem, where they serve as food for birds and other animals. The fact that they’re able to survive in such cold environments, where few other creatures could thrive, is a testament to the amazing adaptability of life in even the harshest of conditions. So, the next time you see little specks hopping on a snowy landscape, you might just be looking at a snow flea, a tiny survivor of the frost.
6. Antarctic Krill – Surviving the Freezing Oceans

Antarctic krill are tiny creatures that live in the frigid waters of the Southern Ocean, and they have an extraordinary ability to survive the freezing cold. These shrimp-like crustaceans are a key part of the Antarctic food web, providing food for larger creatures like penguins, seals, and whales. Despite the icy waters they call home, krill have evolved antifreeze proteins that prevent their bodies from freezing, even when temperatures plummet well below zero. These proteins act as a shield against ice formation in their bodies, allowing them to thrive in waters that hover just above freezing. Krill play a crucial role in the Antarctic ecosystem, and their ability to endure freezing temperatures is a vital adaptation that allows them to survive in one of the harshest environments on Earth. By surviving in such cold conditions, krill help sustain the entire food web that exists in the icy waters of the Antarctic. Even though they are small, these creatures are tough, and they manage to find food and reproduce in some of the coldest and most hostile environments on the planet. Krill may not be the first creature that comes to mind when thinking of survival in the cold, but their ability to endure the freezing oceans of the South Pole is truly impressive. They’re living proof that even the smallest creatures can thrive in conditions that would freeze most other animals solid.


