1. Strategic City-State Governance

Singapore stands as a remarkable anomaly in the modern world because it is one of only three true city-states left on the planet. Alongside Monaco and the Vatican City, this island nation operates without the layers of local or provincial government that often slow down larger countries. Since its modern founding by Sir Stamford Raffles in 1819 and its subsequent independence on August 9, 1965, the nation has refined a system where the government acts as both a local city council and a national authority. This compact structure allows leaders to make big decisions very quickly. When a new law or a major infrastructure project is proposed, it does not get stuck in years of red tape. Instead, the civil service works with a unified purpose to turn ideas into reality, making Singapore a global leader in administrative efficiency and legislative speed.
The political landscape has been defined by the People’s Action Party (PAP), which has been in power since 1959. This was the year Singapore gained self-governance from British rule, and under the leadership of Lee Kuan Yew, the party began a journey of radical transformation. While some critics argue that having one party in power for so long limits political debate, others point to the incredible stability it provides. Because the government does not have to worry about being replaced every few years, it can plan projects that span decades, such as long-term water security and massive urban redevelopments. This continuity is a key reason why the nation evolved from a small trading post into a first-world powerhouse in just one generation, proving that a clear and consistent vision can produce extraordinary results for a population.
2. A Global Financial Powerhouse
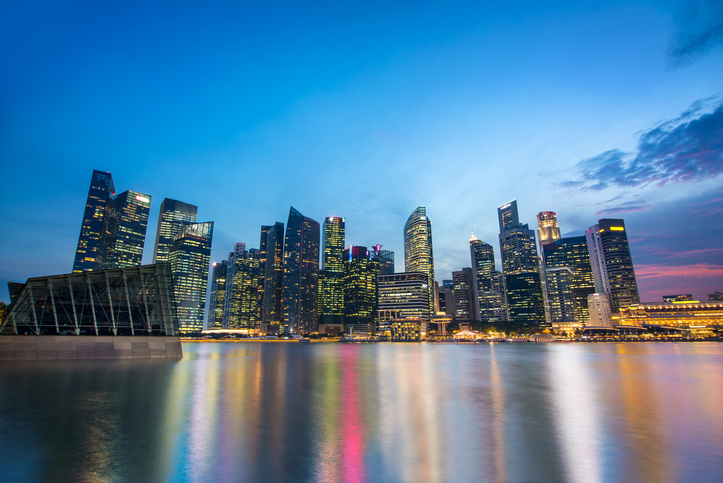

Singapore has earned its reputation as a “Little Red Dot” that carries massive economic weight. Despite being smaller than many major global cities, it holds one of the highest GDP per capita rates in the world. Since the late 1960s, the government has worked tirelessly to make the island an attractive place for international banks and tech firms. By creating a transparent legal system and offering business-friendly taxes, they turned the country into a magnet for wealth. Today, it serves as the primary gateway for investors looking to enter the Asian market. The Singapore Exchange (SGX), which opened in 1999, is a central hub for trading, and the nation’s currency is viewed as one of the most stable and reliable in the world, reflecting the deep trust that global markets have in Singaporean leadership.
What makes this financial success even more impressive is the fact that Singapore has almost no natural resources of its own. In the early years after 1965, the country had to import everything from construction sand to the water people drank. Instead of relying on land or minerals, the nation invested heavily in its people through education and specialized training. By focusing on high-value industries like pharmaceuticals, electronics, and aerospace engineering, they created a “knowledge economy.” They also utilized their geographic location along the Strait of Malacca to build one of the world’s busiest ports. This clever mix of strategic positioning and smart policy ensures that even without oil or gold, Singapore remains an essential player in the global supply chain and a top destination for the world’s most talented innovators.
3. Multicultural Harmony in Policy and Practice
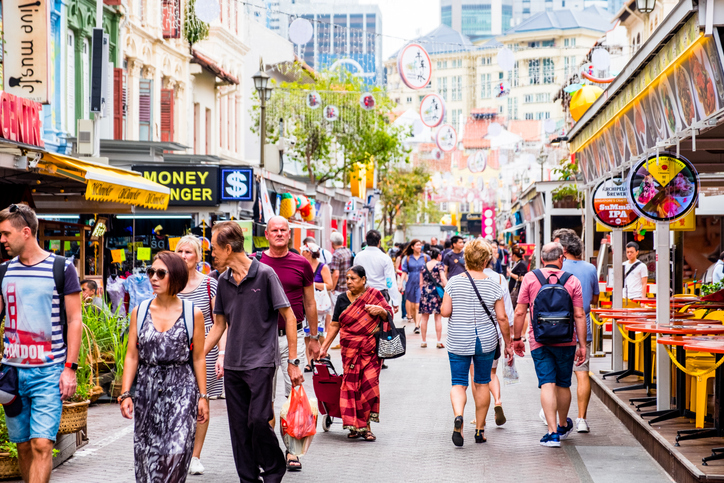

The social fabric of Singapore is a colorful tapestry made of different races and religions living closely together. The government recognizes four official languages: English, Malay, Mandarin, and Tamil. This policy was established early on to ensure that no single ethnic group felt excluded from the national identity. English was chosen as the main language for business and schools to provide a neutral ground for everyone to communicate while also connecting the country to the global economy. You will see this diversity everywhere, from the street signs to the national anthem, which is sung in Malay. This commitment to inclusion is not just a polite gesture but is actually written into the laws of the land to prevent the kind of racial tension that many other diverse nations face.
To keep the peace and build a shared culture, the state organizes many events that celebrate different heritages. For example, the “Speak Good English Movement” was launched in 2000 to help citizens master standard English, yet the government also understands the charm of “Singlish,” which is a unique local blend of various dialects. Throughout the year, festivals like Chinese New Year, Hari Raya, Deepavali, and Christmas are celebrated by the whole nation. In public housing, there are even quotas to ensure that people from different backgrounds live on the same floors and shop at the same markets. By making sure people interact every day, the government helps build a society where respect is the default setting. This intentional approach to harmony has turned a potentially divided population into a strong, united community.
4. Urban Planning with Nature in Mind
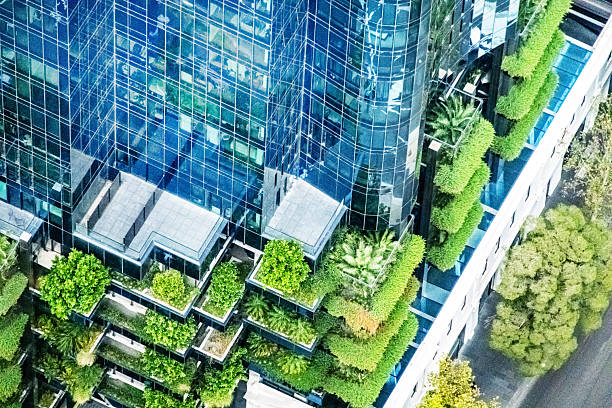

Visitors often call Singapore a “City in a Garden,” and this is the result of a very specific plan that started in the 1960s. Back then, Lee Kuan Yew insisted that greening the city would make life better for residents and show investors that the country was well-managed. Today, this vision is managed by the National Parks Board, which looks after more than two million trees across the island. Every single one of these trees is tracked with GPS technology and has its own digital ID so that workers can monitor its health and growth. This high-tech approach to nature ensures that even as the city grows taller with skyscrapers, it also grows greener. It is common to see plants growing off the sides of buildings or massive “Supertrees” that collect rainwater and provide shade.
Living in a tropical climate can be very hot, but Singapore’s urban planners use nature to fight the heat. By planting specific types of trees and creating lush parks like the Singapore Botanic Gardens,which became a UNESCO World Heritage site in 2015,they have successfully lowered the temperature in urban areas. These green spaces do more than just look pretty; they filter the air and provide a home for local wildlife like otters and exotic birds. The government also requires new buildings to replace any greenery they take away with rooftop gardens or vertical forests. This ensures that the concrete jungle never takes over the natural landscape. By treating nature as a vital part of the city’s infrastructure, Singapore has created a beautiful and sustainable environment that serves as a model for future cities worldwide.
5. Land Reclamation and Ingenious Use of Space
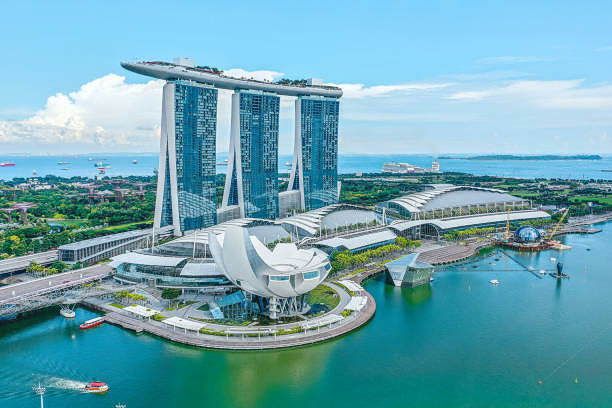

Because Singapore is so small, it has had to literally grow its own land to survive. Since its independence, the country has increased its physical size by about 25 percent through a process called land reclamation. This involves filling in coastal areas with sand and earth to create new ground for buildings and parks. If you visit the famous Marina Bay Sands or the massive Changi Airport, you are actually standing on land that used to be under the ocean. This massive engineering effort has been going on for decades, with major milestones like the East Coast Reclamation project that began in 1966. By expanding its borders outward, the nation has found enough space to house its growing population and build world-class facilities without feeling overcrowded.
Managing such a tiny space requires a level of planning that is almost like a game of chess. Every square meter of land is carefully assigned a purpose by the Urban Redevelopment Authority. They look decades into the future to decide where factories, homes, and parks should go. This foresight is also helping the country prepare for climate change and rising sea levels. Many of the newer reclaimed areas are built at higher elevations to protect against flooding in the future. Singapore also explores underground options, building massive caverns to store oil and water so that the surface remains free for people to use. This clever and persistent use of space shows that a country does not need a huge territory to be a global giant; it just needs to use what it has with incredible intelligence.
6. Public Housing as Social Policy
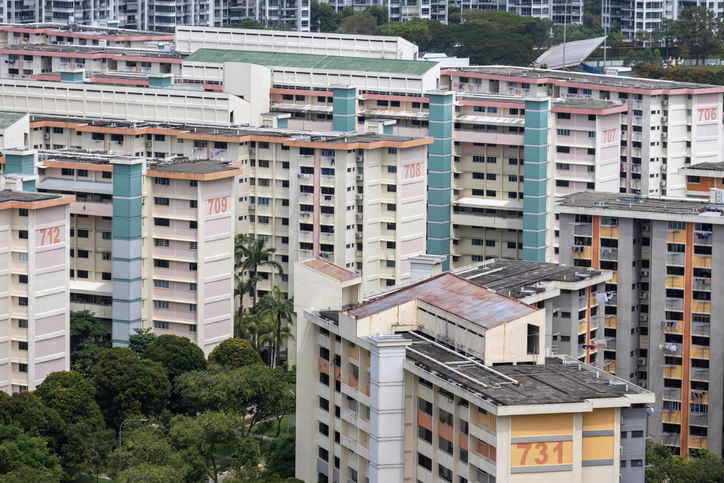

One of the most impressive achievements in Singapore is its public housing system, which provides homes for over 80 percent of the population. Unlike many other countries where public housing is often seen as a last resort for the poor, Singapore’s Housing and Development Board (HDB) flats are high-quality homes that people are proud to own. This program started in 1960 to solve a massive housing crisis and get people out of crowded slums. Today, the government encourages people to buy their flats using their mandatory savings, which gives almost every citizen a personal stake in the country’s success. This sense of ownership is a major reason why neighborhoods are so well-maintained and why there is such a strong sense of community among the residents.
These housing estates are designed to be “towns within themselves,” meaning they have schools, grocery stores, clinics, and playgrounds all within walking distance. The government also uses these buildings to promote social harmony by using an “Ethnic Integration Policy.” This rule ensures that every block of flats has a balanced mix of Chinese, Malay, and Indian residents, preventing the formation of ethnic ghettos. By living side-by-side, neighbors of different backgrounds share meals, celebrate holidays together, and build lasting friendships. This makes public housing much more than just a place to sleep; it is a powerful tool for social engineering that keeps the nation stable and fair. The HDB system is a shining example of how a government can use infrastructure to improve the daily lives and the social unity of its people.
7. Efficient Public Transport System
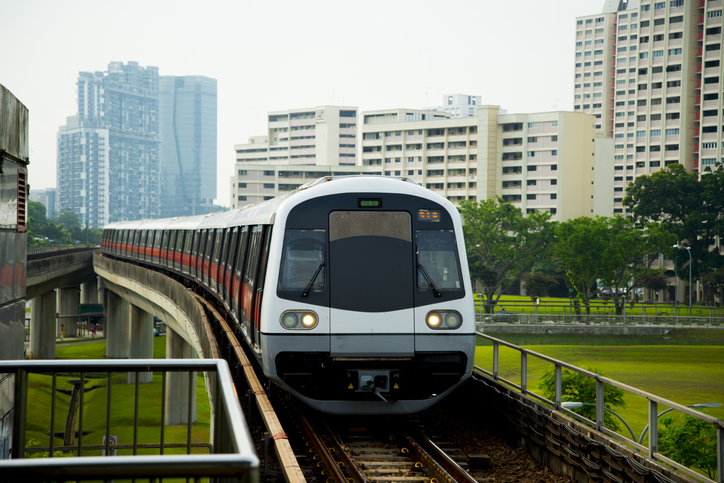

Getting around Singapore is incredibly easy thanks to a world-class public transport network that is famous for being clean and punctual. The heart of this system is the Mass Rapid Transit (MRT), which first opened its doors to the public in November 1987. Since then, the rail network has expanded to cover almost every corner of the island, making it possible for millions of people to commute without ever needing a car. The trains and buses are timed perfectly, and commuters can use smart apps to see exactly when the next ride will arrive. This efficiency is a top priority for the government because it reduces traffic jams and lowers the city’s carbon footprint, making the air cleaner for everyone who lives there.
The government also makes it very expensive to own a private car to keep the roads clear. Instead of everyone driving, the state invests billions of dollars into making public transit the most convenient option. They use a “hub and spoke” model where major train stations are connected to bus interchanges, allowing for a seamless journey from your front door to your office. Recent upgrades include driverless trains and stations that are integrated with shopping malls and libraries. By focusing on smart technology and constant maintenance, Singapore has created a transport culture where people actually prefer the train over driving. This focus on mobility ensures that the city stays productive and that people spend less time stuck in traffic and more time with their families or at work.
8. World-Class Education System

Singapore’s education system is often ranked as the best in the world, particularly in subjects like math and science. The country’s philosophy is that since they have no natural resources, their people must be their greatest asset. From a very young age, students are taught to be disciplined, hardworking, and creative. The Ministry of Education sets very high standards for both students and teachers, ensuring that everyone has access to a top-tier learning environment. Since the nation became independent in 1965, the focus has shifted from basic literacy to advanced high-tech skills. Today, schools use the latest technology and modern teaching methods to prepare kids for the jobs of the future, ensuring the workforce remains competitive in a global market.
The system is also designed to be meritocratic, meaning that success is based on how hard you study and your actual abilities rather than how much money your family has. The government provides many scholarships and financial aid programs to make sure that talented students from humble backgrounds can attend the best universities. In recent years, there has been a move to reduce the stress of exams and encourage students to find their own unique passions, whether in the arts, sports, or vocational skills. This flexibility shows that the system is evolving to meet the needs of a modern society. By constantly updating the curriculum and investing in teacher training, Singapore ensures that its citizens are ready to lead and innovate on the world stage for many generations to come.
9. Strict but Purposeful Laws

Singapore is well-known for having very strict laws that keep the city exceptionally safe and clean. You might have heard that it is illegal to sell chewing gum or that you can be fined for littering or eating on the subway. While these rules might seem unusual to outsiders, they are part of a cultural belief that everyone should respect public spaces. These laws were introduced in the late 1960s and 1970s to transform the city into a modern, orderly metropolis. Because the rules are applied fairly to everyone, there is a very high level of trust in the police and the legal system. The result is one of the lowest crime rates in the world, allowing people to walk alone at night without any fear.
The legal system also plays a big role in how the city is organized and run. There are strict rules about building heights, where people can smoke, and even how much noise you can make in certain areas. These regulations are not meant to be annoying; they are designed to make living in a high-density city more comfortable for everyone. By having clear expectations for behavior, the government reduces conflict between neighbors and ensures that the city functions like a well-oiled machine. This focus on “law and order” has made Singapore a very predictable and stable place for international families and businesses to call home. It proves that when everyone follows a common set of rules, the entire community benefits from a higher quality of life and a greater sense of security.
10. Sustainability at National Scale

For a tiny island with limited land, sustainability is not just a trend; it is a matter of national survival. Singapore has developed an incredible water management system known as the “Four National Taps” to make sure it never runs out of fresh water. This includes collecting rainwater in huge reservoirs, importing water from neighboring Malaysia, and using high-tech desalination plants. Perhaps most impressively, they have a system called “NEWater,” which was launched in 2003 to recycle wastewater into ultra-clean, high-grade reclaimed water that is safe to drink. This innovation has made Singapore a world leader in water technology and has given the country the independence it needs to grow without worrying about droughts or political disputes over resources.
Beyond water, the nation is working hard to become a “Green Plan 2030” leader by reducing its carbon emissions and switching to cleaner energy. Since the country does not have much space for large wind farms, it is getting creative by putting solar panels on the roofs of public housing and even floating them on reservoirs. The government also encourages businesses to adopt “green” buildings that use less electricity and water. By testing these new technologies on a small scale, Singapore acts as a living laboratory for the rest of the world. These efforts show that even a small nation can make a big impact on the environment. By planning for the long term and investing in the latest science, Singapore is ensuring that it remains a healthy and vibrant place to live for many years to come.
11. Meritocracy as National Creed

The idea of meritocracy is the backbone of Singaporean society and the primary way the country is run. This means that a person’s success is determined by their hard work and talent rather than who their parents are or how much money they have. This principle was championed by the founding fathers after the nation gained independence in 1965 to ensure the best minds were leading the country. In the early years, competitive exams and scholarships were used to find bright students from every neighborhood and give them the best possible education. This approach created a highly skilled workforce and a government filled with experts, which helped the tiny island compete with much larger nations on the global stage.
As the country has matured, the government has updated its view of meritocracy to make it more inclusive. In recent years, specifically around 2021, the Ministry of Education began moving away from the rigid PSLE scoring system to reduce pressure on young children. They now focus on “multiple pathways” to success, recognizing that talent exists in many forms including the arts, sports, and technical skills. This shift shows that while Singapore still believes in rewarding excellence, it also understands that society needs a diverse range of skills to thrive. By adapting this core value, the nation ensures that everyone has a fair chance to contribute to the economy and that the social ladder remains open to anyone willing to put in the effort.
12. A Data-Driven Government

Singapore is often called a “Smart Nation” because of how it uses technology and data to make daily life better for its citizens. The Smart Nation initiative was officially launched in November 2014 with the goal of using digital innovation to solve urban problems. Today, the government uses sensors and big data to monitor everything from traffic flow on the roads to the water levels in the drains. This evidence-based approach means that decisions are not made on guesses or opinions but on actual facts. For instance, if data shows that a certain bus stop is getting too crowded at 8:00 AM, the transport authority can quickly adjust the schedule to send more buses, making the commute smoother for everyone.
This reliance on data extends to public health and urban safety as well. During the global health challenges of 2020, Singapore was a pioneer in using digital tools like “TraceTogether” to keep the community safe. The government also uses 3D digital twins of the entire island to simulate how new buildings might affect wind flow or temperature in a neighborhood before they even start construction. While the state collects a lot of information, it also has very strict cybersecurity laws to protect the privacy of its people. By combining high-tech tools with careful planning, Singapore runs a city that is not only efficient but also highly responsive to the needs of the people, ensuring that public services are always improving.
13. National Service as Social Glue

For young men in Singapore, National Service (NS) is a significant rite of passage that has been a part of life since the National Service (Amendment) Bill was passed in 1967. This policy requires all male citizens and permanent residents to serve in the military, police, or civil defense for a period of two years. While its main goal is to ensure the island is always ready to defend itself, it serves an even deeper purpose as “social glue.” In the barracks and training fields, young men from different ethnic backgrounds and income levels live and work together. This creates a shared bond and a common identity that helps break down social barriers, making the country more united and stable.
The government views National Service as a vital way to instill discipline, leadership, and a sense of duty to the nation. Over the decades, the system has evolved to include more specialized roles in areas like cybersecurity to meet modern challenges. Even after their full-time service ends, men continue to return for annual training as “Operationally Ready National Servicemen” until they are in their 40s. This commitment ensures that the population remains connected to the defense of their home. Many Singaporeans believe that this shared experience is what makes the country’s diverse society work so well. By asking citizens to contribute to national security, the state reinforces the idea that the peace and prosperity of the nation are everyone’s responsibility.
14. Healthcare Built on Shared Responsibility
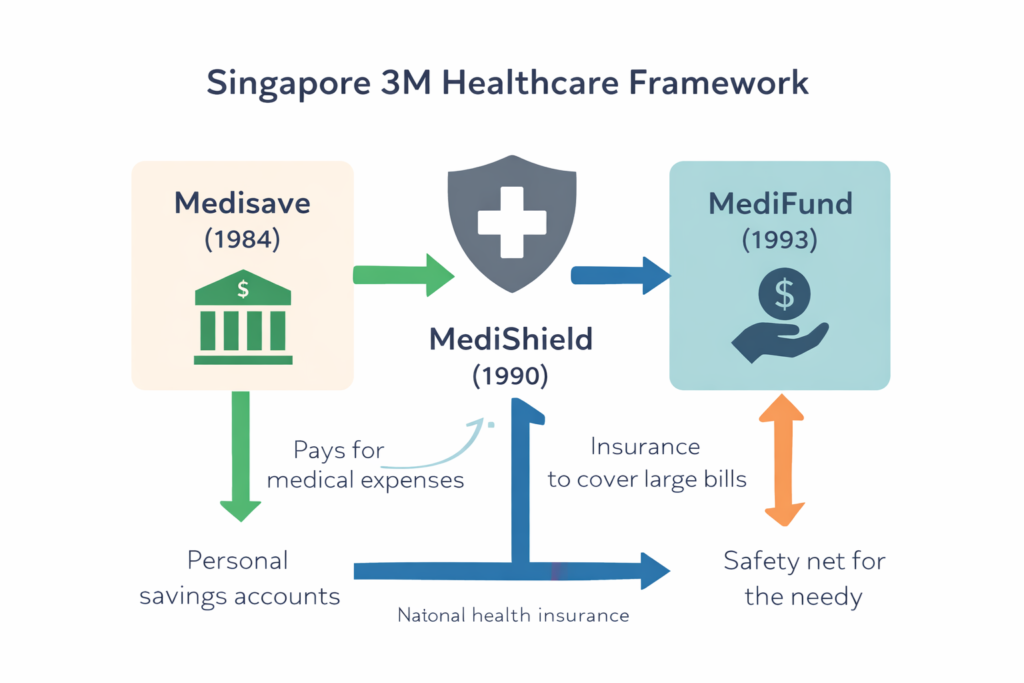
Singapore’s healthcare system is globally respected for providing excellent results at a much lower cost than many other wealthy nations. The system is built on a “shared responsibility” model, which means the government and the individual both play a part in paying for medical care. This was institutionalized through the “3M” framework: Medisave (started in 1984), MediShield (1990), and MediFund (1993). Medisave is a mandatory savings account where workers put aside a portion of their income for future medical needs. This encourages people to stay healthy and make smart choices about their care because they are using their own savings, while the government provides subsidies to keep basic services affordable for everyone.
To make sure no one is left behind, the state provides a safety net called MediFund for those who cannot afford their bills even with subsidies. The government also keeps a very close eye on the price of medicines and hospital services to prevent costs from spiraling out of control. Recently, the nation has launched the “Healthier SG” initiative to focus more on preventive care, encouraging citizens to see a regular family doctor to catch illnesses early. This proactive approach helps people live longer, healthier lives and reduces the long-term burden on the public health system. By balancing personal accountability with strong government support, Singapore has created a healthcare model that is both sustainable for the economy and compassionate for the people.
15. Long-Term Economic Planning
While many countries plan their budgets one year at a time, Singapore looks decades into the future. The government uses “Industry Transformation Maps” to decide which parts of the economy should grow next. For example, back in the early 2000s, the nation decided to become a global leader in biotechnology and invested billions into the Biopolis research hub. This wasn’t a quick fix but a long-term bet that paid off, creating thousands of high-paying jobs for locals. By anticipating where the world is going,whether it is toward green energy, artificial intelligence, or advanced manufacturing,Singapore makes sure its workforce is always ready for the next big thing.
This planning is managed by agencies like the Economic Development Board (EDB), which was founded in 1961. They work closely with schools and universities to make sure that what students are learning in the classroom matches the skills that new companies will need. This coordination is the reason why major global brands like Google, Dyson, and Pfizer choose to put their regional headquarters in Singapore. The government also keeps a “rainy day fund” known as the National Reserves, which are managed by GIC and Temasek. These funds are used to invest in the future and provide a cushion during economic downturns. This disciplined and patient approach to money management ensures that the country remains wealthy and stable regardless of what is happening in the global economy.
16. Controlled Political Pluralism

Singapore operates as a parliamentary democracy, but it has a very unique political style that prioritizes stability and long-term goals. Since the first general election after independence in 1968, the People’s Action Party (PAP) has maintained a strong majority in Parliament. This has allowed the government to pass laws and implement big changes without the constant political gridlock seen in other countries. However, the system has built-in ways to ensure different voices are heard. For example, the “Non-Constituency Member of Parliament” (NCMP) scheme was introduced in 1984 to make sure there is always an opposition presence in the house, even if they didn’t win their specific seats.
In recent years, the political landscape has become more diverse. More opposition members have been elected to Parliament, and the government has increased its focus on public consultation through “Reach” and various town hall meetings. While the laws regarding protests and public speeches are stricter than in some Western countries, the state argues that this is necessary to prevent social unrest in such a small and diverse island. The goal is to have “controlled pluralism,” where different opinions can be shared in a respectful and orderly way. This style of governance ensures that while the country evolves and listens to its citizens, it never loses the stability that has made its economic and social success possible over the last six decades.
17. Cleanliness as Civic Culture

One of the first things people notice when they land at Changi Airport is how incredibly clean the entire country is. While it is true that there are fines for littering, the “Keep Singapore Clean” campaign, which was launched by the Prime Minister in 1968, has turned cleanliness into a national habit. In schools, students are taught from a young age to clean their own classrooms and common areas. This builds a sense of pride and ownership in the environment. By making cleanliness a part of the culture, the government reduces the amount of money it has to spend on street cleaning and trash collection, allowing those funds to be used for more important things like healthcare or education.
The focus on a clean city also has a direct impact on public health and tourism. A clean environment means fewer pests and diseases, which was a major concern for the nation in the mid-20th century. Today, the “SG Clean” quality mark, introduced in 2020, ensures that public spaces like hawker centers and shopping malls follow very high standards of hygiene. This commitment to a spotless city makes Singapore a very pleasant place to live and a top destination for travelers from all over the world. It shows how a simple civic value,taking care of shared spaces,can have massive benefits for a country’s reputation and the well-being of its citizens. Cleanliness is not just about looks; it is a reflection of a well-organized and respectful society.
18. Crisis Management by Design

Singapore is a nation that is always prepared for the worst-case scenario. Because it is a small island with no natural resources, the government knows that it must be ready to handle any crisis, whether it is a financial crash, a pandemic, or a natural disaster. This “crisis management by design” means that every government agency has a plan ready to go at a moment’s notice. For example, the country maintains a strategic stockpile of essential items like rice, masks, and fuel. These plans are not just written on paper; they are practiced regularly through national drills to make sure everyone knows exactly what to do when an emergency happens.
A great example of this preparation was seen in the way Singapore handled the SARS outbreak in 2003 and later global health events. The lessons learned from those experiences led to the building of the National Centre for Infectious Diseases, which opened in 2018. This facility is a world-class hub designed specifically to handle large-scale health crises. The government also communicates very clearly with the public during a crisis, providing daily updates and clear instructions to keep people calm and informed. By being proactive instead of reactive, Singapore is able to bounce back from challenges much faster than many other countries. This resilience is a key part of how the nation is run, ensuring that even in difficult times, the people feel safe and the economy remains strong.
In summary, Singapore is a nation that operates with a level of precision and foresight that is rarely seen elsewhere.


