1. Influencing the Next Generation of Robotics

The movement of poisonous frogs—particularly their ability to grip surfaces, leap efficiently, and navigate slippery terrain—is inspiring new designs in robotics and artificial intelligence, according to Cambridge University Press. Engineers have been analyzing how frogs move and balance to create robots that can climb walls, jump extreme distances, and even move through hazardous environments without slipping. This research is particularly useful in developing rescue robots, which could be deployed in earthquakes, collapsed buildings, or even space exploration missions.
In addition to movement, scientists are studying frog muscles and nerve structures to create biohybrid robots, which blend organic tissue with mechanical components. These frog-inspired systems could lead to next-generation prosthetics, soft robotics, and even robotic exoskeletons that mimic the efficiency and adaptability of living creatures. As robotics continue to evolve, the natural mechanics of poisonous frogs could play a huge role in shaping autonomous machines of the future.
2. Revolutionizing Heart Disease Treatments

Heart disease is the leading cause of death worldwide, affecting millions of people every year. But surprisingly, poisonous frogs may hold the key to groundbreaking new treatments for heart conditions, particularly those related to irregular heartbeats and arrhythmias. These frogs contain compounds that alter sodium and potassium channels in the body, which play a crucial role in controlling heart rhythm and muscle contractions. Unlike traditional heart medications that come with dangerous side effects, frog-derived compounds are highly selective, meaning they target the heart’s electrical system with precision.
Scientists have been studying how these toxin-modified sodium channels work to create new drugs that can regulate heartbeats, reduce the risk of sudden cardiac arrest, and prevent life-threatening arrhythmias. The goal is to develop a next-generation heart medication that can be used to stabilize patients after heart attacks, manage chronic conditions, and improve blood circulation without the negative side effects of current treatments, according to PubMed Central. If these frog-based compounds can be harnessed successfully, they could prolong millions of lives and make heart disease far less deadly in the future.
3. Developing Super Strong, Waterproof Coatings

The skin of poisonous frogs is a scientific marvel—it’s waterproof, bacteria-resistant, and self-cleaning, allowing these tiny creatures to thrive in humid rainforests without getting sick or dehydrated. One company, FROGSKIN, has developed a waterproofing sealer that they claim lasts five times longer than other brands. Researchers have been studying these properties to develop ultra-durable coatings that could be applied to medical equipment, outdoor gear, vehicles, and even buildings. Unlike artificial waterproofing materials, which degrade over time, frog-inspired coatings use nanostructures that repel water while preventing dirt and bacteria from sticking.
This innovation has potential applications in healthcare, transportation, and even space exploration. Imagine hospital surfaces that kill bacteria on contact, reducing infections in surgery rooms. Or self-cleaning car windshields that never need wipers, even in the heaviest rain. Scientists are also exploring how these coatings could improve airplane exteriors, preventing ice buildup on wings and improving fuel efficiency by reducing surface drag. If perfected, this technology could lead to safer, longer-lasting, and more efficient materials in industries around the world.
4. Designing Cutting-Edge Neurological Treatments

Neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and ALS remain some of the most devastating medical conditions, with no true cure in sight. However, the toxins found in poisonous frogs are showing promise in helping to protect and repair nerve cells, potentially leading to new treatments for brain disorders, according to PubMed Central. Certain compounds in their venom can regulate nerve activity, preventing the kind of misfiring and cell death that occurs in patients with neurodegenerative diseases.
Researchers are now testing frog-derived chemicals to develop drugs that slow or even halt neurological decline. These compounds work by modulating nerve signals and preventing toxic protein buildup, two key issues in diseases like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s. If successful, these discoveries could lead to revolutionary treatments that help millions of patients maintain brain function well into old age, potentially reducing the devastating impact of memory loss and motor decline.
5. Creating Non-Addictive Painkillers Stronger Than Morphine

For decades, opioid painkillers like morphine and oxycodone have been some of the most effective ways to manage pain, but they come with a deadly trade-off: addiction, dependence, and overdose risk. Scientists looking for alternatives have turned to poison dart frogs, whose toxins have shown the ability to completely block pain signals—without the addictive effects of opioids. The key lies in a chemical called epibatidine, which was first discovered in the skin of a small Ecuadorian frog. This compound is 200 times more powerful than morphine, yet it works through an entirely different mechanism, preventing pain signals from reaching the brain without activating opioid receptors.
By modifying epibatidine’s structure, researchers are working on developing non-addictive pain medications that could revolutionize treatments for chronic pain, post-surgical recovery, and severe injuries. Unlike opioids, these frog-inspired drugs do not cause tolerance buildup, meaning that patients wouldn’t need higher and higher doses over time. If successful, these compounds could become a game-changer in medicine, offering a powerful painkiller that eliminates suffering without causing addiction or overdose, something that has long been an unsolved problem in modern medicine.
6. Improving Surgical Adhesives for Safer, Stronger Wound Healing

One of the most remarkable abilities of poisonous frogs is how their skin secretes natural adhesives that help them cling to surfaces in humid, wet environments, according to The Conversation. Scientists studying these secretions have discovered that they contain biological polymers that could be the key to creating stronger, safer, and more flexible surgical adhesives. Unlike traditional stitches or staples, which can be rigid, cause infections, or tear delicate tissues, frog-inspired adhesives could allow doctors to seal wounds quickly and effectively, even in areas prone to movement, like the lungs, heart, or intestines.
These adhesives would work by mimicking the frog’s natural ability to adhere to wet surfaces, meaning they could even be used in internal surgeries or as an alternative to sutures for deep wounds and severe injuries. This breakthrough could revolutionize emergency medicine, battlefield trauma treatment, and delicate operations like organ transplants. Since these materials are biodegradable, they would naturally dissolve as the wound heals, eliminating the need for painful stitch removal. If widely adopted, frog-inspired adhesives could drastically improve patient recovery times, reduce infections, and make surgeries safer worldwide.
7. Creating Self-Cleaning Medical Equipment and Clothing

Hospitals and medical facilities face a constant battle against bacteria and infections, with thousands of deaths each year caused by hospital-acquired infections. Poisonous frogs may hold the key to solving this problem—scientists have discovered that their skin produces antimicrobial peptides, which naturally repel bacteria, fungi, and viruses. Unlike traditional antibiotics, which bacteria can develop resistance to, these frog-derived compounds destroy harmful microbes by breaking down their cell walls, making them nearly impossible to resist.
Researchers are working to incorporate these frog-inspired compounds into medical equipment, clothing, and even wound dressings to create self-cleaning surfaces that continuously kill germs without the need for harsh disinfectants. Imagine surgical gloves that never need sterilizing. hospital scrubs that repel bacteria, or bandages that actively fight infections—all thanks to frog biology. This technology could significantly reduce post-surgical infections, help combat antibiotic resistance, and improve hygiene in hospitals, nursing homes, and emergency response settings.
Click here for more stories like this
8. Helping to Develop Ultra-Light, Super-Strong Materials

Scientists are also taking inspiration from poisonous frogs’ skeletons and muscle structures to design new materials that are both lightweight and incredibly strong. Despite their small size, some species of these frogs have dense, flexible bones and muscles that allow them to leap great distances, absorb shock upon landing, and withstand intense pressure. Engineers are now studying how their tissue composition works to create new synthetic materials that could be applied to spacecraft, sports equipment, and even military armor.
By mimicking the frog’s biological durability, researchers hope to develop materials that are both ultra-light and impact-resistant—a key goal in aerospace engineering and protective gear manufacturing. These materials could lead to stronger, more flexible aircraft wings, lightweight yet bulletproof armor for soldiers, and even athletic wear that enhances performance while reducing strain on the body. The applications are nearly endless, and these frog-inspired innovations could soon find their way into everything from NASA’s next-generation spacecraft to the shoes and helmets of professional athletes.
9. Transforming How We Preserve and Store Medicines

Many life-saving drugs, including vaccines, insulin, and organ transplant medications, require strict temperature control to remain effective, making their distribution a huge challenge in remote areas. Scientists are now looking at how poison dart frogs retain and regulate toxins in their bodies without them degrading, hoping to apply the same principles to medicine preservation. These frogs store some of the most powerful natural poisons on Earth for long periods without losing potency, leading researchers to investigate whether their biological mechanisms can be adapted for pharmaceutical storage.
If successful, this discovery could allow critical medications to be stored for longer periods at room temperature, eliminating the need for refrigeration in remote or disaster-stricken areas. This would be a game-changer for global healthcare, enabling life-saving drugs to reach millions of people who currently lack access to proper medical facilities. Imagine a future where vaccines can be stockpiled and transported anywhere in the world without special cooling systems, all thanks to the way frogs naturally preserve their own biochemical defenses.
10. Enhancing Security with Frog-Inspired Toxin Detection Sensors

Security and defense agencies around the world are constantly searching for better ways to detect poisons, toxins, and chemical threats. Scientists studying poisonous frogs’ skin receptors have found that they are incredibly sensitive to even the tiniest amounts of toxic compounds, allowing them to detect chemical changes in their environment with extreme precision. This has led to the development of frog-inspired chemical sensors that could be used to detect bioterrorism agents, environmental toxins, and even food contamination.
These sensors work by mimicking the frog’s natural toxin-detection ability, allowing them to identify dangerous chemicals in the air, water, or on surfaces in real time. This technology could be integrated into airport security systems, military defense networks, or food safety inspections, providing an early warning system for potential chemical threats. With these advancements, a frog’s ability to sense danger in the wild could soon be used to keep millions of people safe from hidden toxins and poisons in everyday life.
11. Advancing Brain-Machine Interfaces for Future Prosthetics
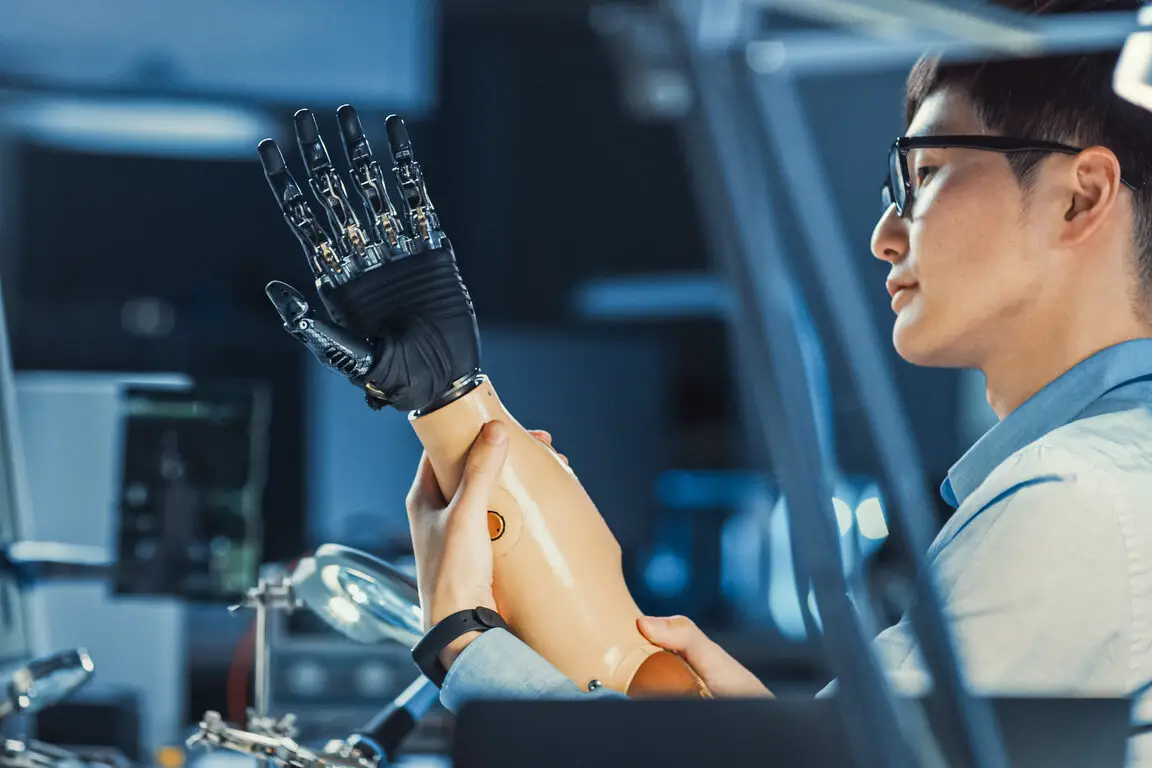
The nervous systems of poisonous frogs have fascinated scientists for years because of how their toxic compounds interact with neural pathways. Certain frog toxins temporarily block nerve signals, leading researchers to explore how they could be used to improve the way prosthetic limbs communicate with the human brain. Current prosthetics often rely on basic electrical signals, but they lack the full sensation and complex movement control of a real limb.
By studying how frog toxins affect neuromuscular function, scientists are designing new brain-machine interfaces that could allow amputees to control artificial limbs with the same precision and sensitivity as natural body parts. This research could lead to fully integrated bionic limbs that restore touch, pressure, and fine motor skills, giving users a level of control never before possible. The insights gained from frog neurology could be the missing link in creating lifelike prosthetics that feel and function just like natural limbs.
12. Helping to Develop New Treatments for Epilepsy and Seizure Disorders

Poisonous frogs produce toxins that directly affect nerve cell activity, making them valuable models for studying neurological disorders like epilepsy and seizures. Their ability to disrupt or modulate electrical signals in the brain has led researchers to explore new drugs that could help control seizures more effectively than existing treatments. Current epilepsy medications often come with severe side effects, but frog-inspired compounds could provide a more targeted approach to calming overactive nerve cells.
Scientists are particularly interested in how frog toxins interact with sodium channels in the nervous system, as this knowledge could lead to highly precise seizure treatments that prevent neuronal overactivity without sedating patients. If this research proves successful, it could provide a major breakthrough in epilepsy treatment, helping millions of people regain a better quality of life with fewer side effects and greater seizure control.
13. Pioneering Advanced Skin Regeneration and Wound Healing

Poisonous frogs have a remarkable ability to heal their skin rapidly, even in harsh, bacteria-filled environments like tropical rainforests. Their skin not only heals quickly, but it also produces natural antimicrobial peptides, which help prevent infections and inflammation. Scientists studying these peptides have discovered that they could be the key to developing advanced wound healing treatments, particularly for burn victims, diabetic ulcers, and post-surgical recovery. Unlike traditional antibiotics, which often become ineffective over time, frog-derived compounds actively destroy harmful bacteria without causing resistance.
This research has led to the development of frog-inspired wound dressings that could speed up healing, reduce scarring, and lower the risk of infections. These specialized bandages mimic the chemical defenses of frog skin, allowing wounds to heal faster while staying protected from harmful bacteria. Some scientists are even exploring whether frog peptides can be used in skin grafts to help burn patients regenerate tissue more efficiently. If widely adopted, these discoveries could lead to revolutionary treatments that drastically improve recovery times for patients suffering from severe injuries or chronic wounds.
14. Redefining How We Understand Paralysis and Muscle Recovery

The toxins in poisonous frogs have a unique effect on muscle control and nerve signals, often leading to temporary paralysis in their predators. While this might sound dangerous, scientists have realized that understanding how these toxins work could lead to major breakthroughs in paralysis treatment and muscle rehabilitation. Certain frog-derived compounds interact with the nervous system in ways that could help reawaken damaged nerve pathways, potentially restoring movement in paralyzed patients.
Researchers are now testing frog-inspired treatments to help stroke survivors regain muscle function and assist those with spinal cord injuries in rebuilding nerve connections. If successful, these discoveries could lead to new therapies that help patients regain mobility, reducing the need for long-term physical therapy and invasive surgeries. Imagine a world where people with paralysis can regain movement simply by using a treatment inspired by a tiny rainforest frog—this could become a reality in the near future.
15. Influencing the Future of Aviation with Aerodynamic Efficiency

It might seem surprising, but poisonous frogs have inspired innovations in aviation as well! Scientists studying their skin texture and muscle mechanics have realized that these tiny creatures have evolved exceptional aerodynamic properties, particularly in their ability to leap great distances with minimal energy use. Researchers are now applying these principles to airplane wing designs, drone technology, and even wind turbine efficiency.
By studying how these frogs generate power, reduce air resistance, and maintain stability in midair, engineers are working on developing more fuel-efficient aircraft and advanced drone systems. Some experiments have already shown that frog-inspired wing structures could reduce turbulence and improve flight stability, potentially leading to quieter, smoother, and more energy-efficient planes. If these findings are applied on a large scale, frog-inspired aviation technology could play a major role in reducing carbon emissions, improving fuel economy, and making air travel more sustainable for the future.


